Table of mobile processors by performance. Processor performance rating from Intel
This material will provide The leading manufacturer of these products is Intel. This company has a dominant positionIn this high-tech market, its semiconductor solutions can be found in almost all its segments.
Why Intel?
As noted earlier, Intel silicon chips form the basis of most electronic devices. Starting with smartphones and tablets, continuing with netbooks, ultrabooks and laptops and ending with high-performance personal computers - most of this technology is based on semiconductor products from this leading manufacturer. Therefore, the performance rating of Intel processors as accurately as possible for eachsegments of this large marketwill allow us to determine the most optimaltechnical specifications. Intel's competitors are focusing on them and, due to this, are trying to catch up with the leading manufacturer of semiconductor products.
Mobile gadgets segment
The performance rating of smartphone processors based on Intel chips includes the latest devices from the ATOM series. This line includes X3, X5 and X7. The least productive in this case are the first semiconductor solutions, and this model range includes C3405 and C3445.
Their technical parameters are identical: 4 computing modules, frequency range 1.2-1.4 GHz, 1 MB cache memory and 28 nm production technology. Key Difference between these two semiconductor products is that the first of them is aimed at use as part of tablets and does not have a module mobile communications, and the second is intended for the smartphone market and is equipped with a cellular transceiver. The X5 line also includes two CPU models: Z8300 and Z8500. They also have 4 code processing units, but these crystals are produced according to 14 nm standards, are equipped with a large cache volume of 2 MB and clock frequencies for the first of them are in the range of 1.44-1.84 GHz, and for the second - 1.44 -2.24 GHz.
The flagship of the X7 line, in this case, is one - Z8700. Its characteristics are almost identical to the X5. The only difference is the clock speeds - 1.6-2.4 GHz. The main technical specifications of this family of processors are given in the table below.
Characteristics of the family of processors for smartphones and tablets
Chip family | CPU model | Frequencies, GHz | Cash, MB | Number of cores, pieces | Technology, nm |
X3 | S3405 | 1.2-1.4 GHz | |||
S3445 |
|||||
X5 | Z8300 | 1,44-1,84 | |||
Z8500 | 1,44-2,24 |
||||
X7 | Z8700 | 1,6-2,4 |
Laptop niche
The level of office solutions is occupied by solutionsCeleron ( models G3900 And G3920).There are no fundamental differences between them. Only in the latter case is it slightly increased from 2.8 GHz to 2.9 GHz. Otherwise, these are excellent chips for creating an office computing system.
The entry level in this case is also occupied by the line’s CPUsPentium ( models G4400, G4500 And G4520).Their performance level is almost identical. These chips are great for basic gaming systems. But in this case the owneryou will have to refuse to run the most demanding games, which due to insufficient hardware specifications will not work on such a PC.
The middle level, as in the case of laptops, is filled with CPUCore i3. Their models are 6100, 6300 and 6320. Their performance is more than enough for comfortable gameplay in any modern game. The main factor that increases productivity is the presence of HT technology and an increase in processing threads program code from 2 to 4.
Processor performance rating from Intel for desktops will not be complete if you lose sight of the CPU seriesi5 And i7. ABOUTThey provide phenomenal performance and allow you to solve all currently possible problems.Models 6400, 6500 and 6600 - for the linei5, 6700 - for ruler i7.
WITH The segment of office-class solutions in this case is occupied by line CPUsCeleron.Maximum autonomy and minimum speed, which is only enough foroffice applications, web surfing and other undemanding tasks, in this case come to the fore. This line includes two CPU models -N3350 And N3450.The key difference between them is the number of computational units. The first chip has only 2 of them, and the second has 4. Accordingly, in the second case the performance will be slightly better.

Laptops entry level based on line CPUsPentiumwhich currently consists of 1 chip -N4200.Improved technical specifications of this processor allow it to demonstrate higher performance. As a result, this chip can even run some games with minimal hardware specifications.
Mid-range mobile computing systems are based on line CPUsCore i3.As in the previous case, only one model belongs to this family of processor devices - 7100U.Improved technical parameters compared to previous chips and the presence of NT technology can significantly increase productivity, in this case it is possible to launch almost all toys. The only exceptions in this case are those that put forward the most stringent requirements for the microprocessor architecture.
N the most powerful laptops are based on chipsi5 And i7.Excellent technical parameters and phenomenal performance allow owners of such computers to solve any problem. In this case, even the latest and most demanding toys will work without any problems.These CPU families are currently represented by the following models: 7200U And 7Y54 For i5 And 7500U And 7Y75 For i7respectively.

Desktops
Processor performance rating for desktop computing systems, much of it duplicates what was previously given for laptops. Only if in the previous case R We were talking about the 7th generation of chips, but in this case the 6th comes to the fore. The update of the CPU model range in this case is planned for January 2017. As a result, the current rating is as follows:

Summary
Within the framework of this material, the currently relevantfrom the leading manufacturer of semiconductor products - Intel. With its help, you can determine the ownership of the device and find out a list of tasks that can be solved with its help.
Intel has come a very long way from a small chip manufacturer to a world leader in processor production. During this time, many processor production technologies were developed, highly optimized technological process and device characteristics.
Many performance indicators of processors depend on the arrangement of transistors on the silicon chip. The technology of transistor arrangement is called microarchitecture or simply architecture. In this article we will look at which Intel processor architectures have been used throughout the company's development and how they differ from each other. Let's start with the most ancient microarchitectures and look all the way to new processors and plans for the future.
As I already said, in this article we will not consider the bit capacity of processors. By the word architecture we will understand the microarchitecture of the microcircuit, the arrangement of transistors on the printed circuit board, their size, distance, technological process, all this is covered by this concept. We will not touch the RISC and CISC instruction sets either.
The second thing you need to pay attention to is the generation of the Intel processor. You've probably heard many times already - this processor is the fifth generation, that one is the fourth, and this one is the seventh. Many people think that this is designated i3, i5, i7. But in fact there is no i3, and so on - these are processor brands. And the generation depends on the architecture used.
With each new generation, the architecture improved, processors became faster, more economical and smaller, they generated less heat, but at the same time they were more expensive. There are few articles on the Internet that would describe all this completely. Now let's look at where it all began.
Intel processor architectures
I’ll say right away that you shouldn’t expect anything from the article. technical details, we will consider only the basic differences that will be of interest to ordinary users.
First processors
First, let's take a brief look at history to understand how it all began. Let's not go too far and start with 32-bit processors. The first was the Intel 80386, it appeared in 1986 and could operate at frequencies up to 40 MHz. Old processors also had a generation countdown. This processor belongs to the third generation, and the 1500 nm process technology was used here.
The next, fourth generation was the 80486. The architecture used in it was called 486. The processor operated at a frequency of 50 MHz and could execute 40 million instructions per second. The processor had 8 KB of L1 cache, and was manufactured using a 1000 nm process technology.
The next architecture was P5 or Pentium. These processors appeared in 1993, the cache was increased to 32 KB, the frequency was up to 60 MHz, and the process technology was reduced to 800 nm. In the sixth generation P6, the cache size was 32 KB, and the frequency reached 450 MHz. The tech process has been reduced to 180 nm.
Then the company began producing processors based on the NetBurst architecture. It used 16 KB of first-level cache per core, and up to 2 MB of second-level cache. The frequency increased to 3 GHz, and the technical process remained at the same level - 180 nm. Already here 64-bit processors appeared that supported addressing more memory. Many command extensions were also introduced, as well as the addition of Hyper-Threading technology, which allowed the creation of two threads from one core, which increased performance.
Naturally, each architecture improved over time, the frequency increased and the technical process decreased. There were also intermediate architectures, but everything has been simplified here a little since that is not our main topic.
Intel Core
NetBurst was replaced in 2006 by Intel architecture Core. One of the reasons for the development of this architecture was the impossibility of increasing the frequency in NetBrust, as well as its very high heat dissipation. This architecture was designed for development multi-core processors, the size of the first level cache was increased to 64 KB. The frequency remained at 3 GHz, but the power consumption was greatly reduced, as well as the process technology, to 60 nm.
Processors based on the Core architecture supported hardware virtualization Intel-VT, as well as some instruction extensions, but did not support Hyper-Threading, since they were developed based on the P6 architecture, where this feature did not yet exist.
First generation - Nehalem
Next, the numbering of generations was started from the beginning, because all the following architectures are improved Intel versions Core. The Nehalem architecture replaced Core, which had some limitations, such as the inability to increase clock frequency. She appeared in 2007. It uses a 45 nm tech process and has added support for Hyper-Therading technology.
Nehalem processors have a 64 KB L1 cache, 4 MB L2 cache and 12 MB L3 cache. The cache is available to all processor cores. It also became possible to integrate a graphics accelerator into the processor. The frequency has not changed, but the performance and size of the printed circuit board have increased.
Second generation - Sandy Bridge

Sandy Bridge appeared in 2011 to replace Nehalem. It already uses a 32 nm process technology, it uses the same amount of first-level cache, 256 MB of second-level cache and 8 MB of third-level cache. Experimental models used up to 15 MB of shared cache.
Also, now all devices are available with a built-in graphics accelerator. The maximum frequency has been increased, as well as overall performance.
Third generation - Ivy Bridge

Processors Ivy Bridge They work faster than Sandy Bridge, and they are manufactured using a 22 nm process technology. They consume 50% less energy than previous models, and also provide 25-60% higher productivity. The processors also support Intel Quick Sync technology, which allows you to encode video several times faster.
Fourth generation - Haswell

The Intel Haswell generation of processor was developed in 2012. The same technical process was used here - 22 nm, the cache design was changed, power consumption mechanisms were improved and performance was slightly improved. But the processor supports many new connectors: LGA 1150, BGA 1364, LGA 2011-3, DDR4 technology, and so on. The main advantage of Haswell is that it can be used in portable devices due to its very low power consumption.
Fifth generation - Broadwell

This is an improved version of the Haswell architecture, which uses the 14 nm process technology. In addition, several improvements have been made to the architecture, which improve performance by an average of 5%.
Sixth generation - Skylake

The next architecture of intel core processors, the sixth generation Skylake, was released in 2015. This is one of the most significant updates Core architecture. To install the processor on the motherboard, use LGA socket 1151, DDR4 memory is now supported, but DDR3 support is retained. Thunderbolt 3.0 is supported, as well as DMI 3.0, which gives twice the higher speed. And by tradition, there was increased productivity, as well as reduced energy consumption.
Seventh generation - Kaby Lake
New, seventh Core generation - Kaby Lake came out this year, the first processors appeared in mid-January. There weren't many changes here. The 14 nm process technology is retained, as well as the same LGA 1151 socket. DDR3L SDRAM and DDR4 SDRAM memory sticks are supported, PCI buses Express 3.0, USB 3.1. In addition, the frequency was slightly increased and the transistor density was reduced. Maximum frequency 4.2 GHz.
conclusions
In this article, we looked at the Intel processor architectures that were used in the past, as well as those that are used now. Next, the company plans to switch to the 10 nm process technology and this generation of Intel processors will be called CanonLake. But Intel is not ready for this yet.
Therefore, in 2017 it is planned to release an improved version of SkyLake under the code name Coffe Lake. It is also possible that there will be other Intel processor microarchitectures until the company fully masters the new process technology. But we will learn about all this over time. I hope you found this information helpful.
about the author
Founder and administrator of the site, I am fond of open software and operating room Linux system. I currently use Ubuntu as my main OS. In addition to Linux, I am interested in everything related to information technology and modern science.
· 02/16/2017
Everyone knows what a processor (CPU) is, as well as its importance. The phrase that this is the “brain” of any computer stuck in my teeth. However, this is true, and the capabilities of a laptop or desktop PC are largely determined by this component. When planning to buy a new computer, you need to understand that one of the main characteristics is the processor. Each model indicates the name of the CPU used and the main characteristics. How can you determine at first glance which one is faster and which one is slower, which one to prefer if you often have to work autonomously, and which processor is better for games? This material is a kind of small guide in which I will tell you what Intel processor markings exist, how to decipher it, determine the generation and series of the processor, and give the main characteristics. Go.
Main characteristics of processors
In addition to the name, each processor has its own set of characteristics, reflecting the possibility of using it for a particular job. Among them the main ones can be noted:
- Number of Cores. Shows how many physical processors are hidden inside the chip. Most laptops, especially those with “U” version processors, have 2 cores. More powerful options have 4 cores.
- Hyper-Threading. A technology that allows you to divide the resources of the physical core into several threads (usually 2) running simultaneously in order to increase performance. Thus, a 2-core processor in the system will appear as a 4-core processor.
- Clock frequency. Measured in gigahertz. In general, we can say that the higher the frequency, the more powerful the processor. Let’s immediately make a reservation that this is far from the only criterion that reflects the performance of the CPU.
- Turbo Boost. Technology that allows you to increase the maximum processor frequency at high loads. Versions "i3" are deprived automatic change frequencies, and this technology is present in “i5” and “i7”.
- Cache. Small (usually 1 to 4 MB) volume high-speed memory, which is an integral part of the processor. Allows you to speed up the processing of frequently used data.
- TDP (Thermal Design Power). Value showing maximum amount heat that must be removed from the processor to ensure normal temperature conditions for its operation. Typically, the higher the value, the more powerful the processor and the hotter it is. The cooling system must cope with this power.
Intel processor markings
The first thing that catches your eye is the marking, consisting of letters and numbers.
What the name is is clear. The manufacturer produces its processors under this trade name. This can be not only “Intel Core”, but also “Atom”, “Celeron”, “Pentium”, “Xeon”.
The name is followed by the processor series identifier. This could be "i3", "i5", "i7", "i9" if we're talking about o "Intel Core", or the characters "m5", "x5", "E" or "N" may be specified.
After the hyphen, the first digit indicates the processor generation. At the moment, the newest is the 7th generation Kaby Lake. The previous generation Skylake had serial number 6.
The next 3 digits are the serial number of the model. In general, the higher the value, the more powerful the processor. So, i3 has a value of 7100, I5 – 7200, i7 is marked as 7500.
The last character (or two) indicates the processor version. These may be "U", "Y", "HQ", "HK" or others.
Processor series
With the exception of budget models of laptops or desktop PCs, the rest use processors of the Core i3, Core i5, and Core i7 series. The higher the number, the more powerful the CPU. For most everyday work applications, an i5 processor will be optimal. A more productive one is needed if the computer is used as a gaming computer, or if it requires special computing power to work in “heavy” applications.
Processor generation
Intel updates generations of its processors approximately every year and a half, although this interval tends to increase to 2-3 years. From the “Tick-Tock” scheme they switched to the “Tick-Tock-Tock” release scheme. Let me remind you that this processor release strategy implies that in the “Tick” step there is a transition to a new technical process, and the changes made to the processor architecture are minimal. In the “So” step, a processor with an updated architecture is produced using an existing technical process.
| № | Name | Supported memory | Technical process | Video card | Year of issue |
| 1 | Westmere | DDR3-1333 | 32nm | — | 2008-2010 |
| 2 | Sandy Bridge | DDR3-1600 | 32nm | HD Graphics 2000 (3000) | 2011 |
| 3 | Ivy Bridge | DDR3-1600 | 22nm | HD Graphics 4000 | 2012 |
| 4 | Haswell | DDR3-1600 | 22nm | HD Graphics 4000 (5200) | 2013 |
| 5 | Broadwell | DDR3L-1600 | 14nm | HD Graphics 6200 | 2014 |
| 6 | Skylake | DDR3L-1600/DDR4 | 14nm | HD Graphics 520 - 580 | 2015 |
| 7 | Kaby Lake | DDR3L-1600/DDR4 | 14nm | HD Graphics 610 (620) | 2016 |
| 8 | Coffee Lake | DDR4 | 14nm | UHD Graphics 630 | 2017 |
The transition to a thinner technical process allows you to reduce power consumption and improve processor performance.
Processor version
This indicator may turn out to be almost more important than simply comparing, say, i3 with i5. If we talk about laptops, in most cases 4 versions of Intel Core processors are used, having different meanings TDP (from 4.5 W in the “Y” version to 45 W for the “HQ”), and, accordingly, different performance and energy consumption. Long battery life depends not only on the processor, but also on the inherent capacity of the battery used.
I will give the versions of Intel Core processors, starting with the most low-power ones.
"Y" / "Core m" - low performance and passive cooling
Used in portable devices and small laptops. Passive cooling allows you to make your computer silent. However, it is not suitable for serious tasks. At the same time, even taking into account the TDP of 4.5 W, the compactness of the devices does not allow for a large battery, which negates all the advantages of low power consumption.
In general, if the task is not to buy something like the Apple MacBook 12 or ASUS ZENBOOK UX305CA, then you should give preference to more powerful processors.
| Model | Clock frequency, GHz | Turbo Boost, GHz | Cash, MB | TDP, W | Video card |
| Core i7-7Y75 | 1.3 | 3.6 | 4 | 4.5 | Intel HD 615 |
| Core m7-6Y75 | 1.2 | 3.1 | 4 | 4.5 | Intel HD 515 |
| Core i5-7Y54 | 1.2 | 3.2 | 4 | 4.5 | Intel HD 615 |
| Core i5-7Y30 | 1.0 | 2.6 | 4 | 4.5 | Intel HD 615 |
| Core m5-6Y57 | 1.1 | 2.8 | 4 | 4.5 | Intel HD 515 |
| Core m3-7Y30 | 1.0 | 2.6 | 4 | 4.5 | Intel HD 615 |
| Core m3-6Y30 | 0.9 | 2.2 | 4 | 4.5 | Intel HD 515 |
"U" - for everyday use
“U” series processors are the best choice for a laptop for every day. This is the best combination of performance, energy consumption and cost. A TDP of 15 W allows you to achieve both the ability to cope with almost any task and get good battery life.
There are modifications of the 7th generation processors with a TDP of 28 W, which use an improved Intel Iris Plus 640 or 650 graphics subsystem.
It is not possible to get by with passive cooling, but this is compensated by performance. The difference from more powerful versions is the presence of only 2 cores, even in the “i7” series.
Examples of processors in the table.
| Model | Clock frequency, GHz | Turbo Boost, GHz | Cash, MB | TDP, W | Video card |
| Core i7-7600U | 2.8 | 3.9 | 4 | 15 | Intel HD 620 |
| Core i7-7660U | 2.5 | 4.0 | 4 | 15 | Iris Plus 640 |
| Core i7-7567U | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4 | 28 | Iris Plus 650 |
| Core i7-7500U | 2.7 | 3.5 | 4 | 15 | Intel HD 620 |
| Core i7-6600U | 2.6 | 3.4 | 4 | 15 | Intel HD 520 |
| Core i7-6567U | 3.3 | 3.6 | 4 | 15 | Iris 550 |
| Core i7-6500U | 2.5 | 3.1 | 4 | 15 | Intel HD 520 |
| Core i5-7200U | 2.5 | 3.1 | 3 | 15 | Intel HD 620 |
| Core i5-7267U | 3.1 | 3.5 | 4 | 28 | Iris Plus 650 |
| Core i5-6287U | 3.1 | 3.5 | 4 | 15 | Iris 550 |
| Core i5-6200U | 2.3 | 2.8 | 3 | 15 | Intel HD 520 |
| Core i3-7100U | 2.4 | — | 3 | 15 | Intel HD 620 |
"HQ" / "HK" - quad-core, high-performance
The best choice if you are looking for a laptop for gaming or working with resource-intensive applications. The “HQ” version has 4 cores, which in combination with Hyper-Threading technology gives 8 threads. Power consumption (TDP) of 45 W is bad for battery life. In order for the laptop to withstand several hours on battery power, it is advisable to choose batteries with a larger capacity, for example, with 6 cells.
“HK” differs from “HQ” in that it has an unlocked multiplier, which makes it possible to engage in “overclocking” by manually increasing operating frequency processor. Similar versions of 7th generation processors were announced only in January 2017, so at the moment almost all laptop models are based on processors of the “HK” and “HQ” versions of the previous, 6th generation. However, we obviously won’t have to wait long for new models.
Examples of processors in the table.
| Model | Clock frequency, GHz | Turbo Boost, GHz | Cash, MB | TDP, W | Cores/threads | Video card |
| Core i7-7920HQ | 3.1 | 4.1 | 8 | 45 | 4/8 | Intel HD 630 |
| Core i7-7820HK | 2.9 | 3.9 | 8 | 45 | 4/8 | Intel HD 630 |
| Core i5-7700HQ | 2.8 | 3.8 | 6 | 45 | 4/8 | Intel HD 630 |
| Core i5-7440HQ | 2.8 | 3.8 | 6 | 45 | 4/4 | Intel HD 630 |
| Core i5-7300HQ | 2.5 | 3.8 | 6 | 45 | 4/4 | Intel HD 630 |
| Core i7-6970HQ | 2.8 | 3.7 | 8 | 45 | 4/8 | Iris Pro 580 |
| Core i7-6920HQ | 2.9 | 3.8 | 8 | 45 | 4/8 | Intel HD 530 |
| Core i7-6870HQ | 2.7 | 3.6 | 8 | 45 | 4/8 | Iris Pro 580 |
| Core i7-6820HQ | 2.7 | 3.6 | 8 | 45 | 4/8 | Intel HD 530 |
| Core i7-6770HQ | 2.6 | 3.5 | 6 | 45 | 4/8 | Iris Pro 580 |
| Core i7-6700HQ | 2.6 | 3.5 | 6 | 45 | 4/8 | Intel HD 530 |
| Core i5-6440HQ | 2.6 | 3.5 | 6 | 45 | 4/4 | Intel HD 530 |
| Core i5-6300HQ | 2.3 | 3.2 | 6 | 45 | 4/4 | Intel HD 530 |
Xeon E – for high-performance workstations
These processors are used in powerful laptops, acting as high-performance workstations. This technique is aimed primarily at those who are engaged in 3D modeling, animation, design, and perform complex calculations where high power is required. The processors have 4 cores and Hyper-Threading technology.
Usually there is no need to talk about the ability to work on batteries for a long time. Autonomy is not the strong point that laptops using such processors have.
Examples of processors in the table.
| Model | Clock frequency, GHz | Turbo Boost, GHz | Cash, MB | TDP, W | Video card | Generation |
| Xeon E3-1535M v6 | 3.1 | 4.2 | 8 | 45 | Iris Pro P630 | 7 |
| Xeon E3-1505M v6 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 8 | 45 | Iris Pro P630 | 7 |
| Xeon E3-1575M v5 | 3.0 | 3.9 | 8 | 45 | Iris Pro P580 | 6 |
| Xeon E3-1535M v5 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 8 | 45 | HD Graphics P530 | 6 |
| Xeon E3-1505M v5 | 2.8 | 3.7 | 8 | 45 | HD Graphics P530 | 6 |
Now I will list the remaining processors that can be found in laptops, but which are not part of the “Intel Core” family.
“Celeron” / “Pentium” - for those who are economical and not in a hurry
| Low cost. Light tasks (web surfing, office programs). | |
| Games, not for serious work. |
You should forget about games (except for very simple), difficult tasks. The destiny of laptops with such processors is leisurely office work and surfing the Internet. You can only give preference to models with a CPU of this level if price is one of the main selection criteria, or if you plan to use Linux or OS from Google. Unlike Windows, the hardware requirements are noticeably lower.
Celeron processors have power consumption ranging from 4 to 15 watts, with those models starting with the letter “N” (such as N3050, N3060, etc.) consuming between 4 and 6 watts. Models with the letter “U” at the end (for example, 2957U, 3855U, etc.) are more productive and their power already reaches 15 W. There is usually no gain in battery life when using the Celeron Nxxxx, since budget laptop models also save on batteries.
Pentium processors are more productive than Celeron, but still belong to the budget segment. Their TDP is at the same level. Battery life can last for several hours, which, while the performance is not as dull as that of the Celeron, allows you to get a very decent office laptop.
These processors come in both dual-core and quad-core variants.
Examples of processors in the table.
| Model | Clock frequency, GHz | Turbo Boost, GHz | Cash, MB | Cores/threads | TDP, W | Video card |
| Pentium N3560 | 2.4 | — | 2 | 2/2 | 37 | HD Graphics |
| Pentium 4405U | 2.1 | — | 2 | 2/4 | 15 | HD 510 |
| Pentium N3700 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2 | 4/4 | 6 | HD Graphics |
| Celeron N2970 | 2.2 | — | 2 | 2/2 | 37 | HD Graphics |
| Celeron 3765U | 1.9 | — | 2 | 2/2 | 15 | HD Graphics |
| Celeron N3060 | 1.6 | 2.48 | 2 | 2/2 | 6 | HD Graphics |
"Atom" - long battery life and dismal performance
Examples of processors in the table.
| Model | Clock frequency, GHz | Turbo Boost, GHz | Cash, MB | Video card |
| Atom x7-Z8700 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2 | HD Graphics |
| Atom x5-Z8500 | 1.44 | 2.24 | 2 | HD Graphics |
| Atom Z3735F | 1.33 | 1.83 | 2 | HD Graphics |
Integrated Graphics
All processors have a built-in video card, which is labeled as “Intel HD Graphics”. For 7th generation processors, the video core marking begins with “6” (for example, HD Graphics 610), for the 6th generation – with “5” (for example, HD Graphics 520). Some top-end processors have a more powerful built-in video card, labeled “Iris Plus”. So, the i7-7600U processor has “on board” Intel video card HD Graphics 620, and the i7-7660U is “Iris Plus 640”.
About serious competition with NVidia solutions or AMD we are not talking about, however, for everyday work, watching videos, simple games or at low settings, you will still be able to have some fun. For more serious gaming requests, a discrete graphics card is required.
UPD. 2018. It's time to add to what has been said. Recently, models have appeared in the line of Intel processors that are marked with the letter “G” at the end. For example, i5-8305G, i7-8709G and others. What's special about them? To begin with, I will say that these CPUs are aimed at use in laptops and netbooks.
Their peculiarity is the use of a “built-in” graphics video processor produced by AMD. This is the joint creativity of two sworn competitors. It’s not for nothing that I put the word “built-in” in quotation marks. Although it is considered one with the processor, physically it is a separate chip, although located on the same substrate as the CPU. AMD ships ready graphic solution, and Intel only installs them on its processors. Friendship is friendship, but the chips are still apart.
“In short, Sklifosovsky!”
“So which processor is best for me,” many will probably ask. A lot has been written, you can get lost in the varieties, characteristics, etc., but you need to choose something. Well, for the impatient, I’ll put everything in one table, which will rank the processors according to their applicability for certain purposes.
| Laptop class | Recommended CPU | Example | Autonomy, hour |
| Workstation/Powerful Gaming | Core i5/i7 HQ | Core i7-7820HK, Core i5-7440HQ | 3-8 |
| Core i7 U | Core i7-7500U | 5-17 | |
| Universal | Core i5U | Core i5-7200U, Core i5-6200U, Core i5-6300U | 5-17 |
| Versatile, with advanced capabilities | Core i7 U | Core i7 8550U | 5-17 |
| Universal | Core i5U | Core i5 8250U, | 5-17 |
| Ultrabook, thin compact | Core m / Core i5 / i7 Y | Core m3, Core i5-7Y54 | 5-9 |
| Budget | Celeron, Pentium | Celeron N3050, Pentium N4200 | 4-6 |
| Tablet, cheap compact laptop | Atom | Atom Z3735F, Atom x5 | 7-12 |
Upd. 2018. Time does not stand still and after the emergence of the new, 8th generation of processors, we have to significantly reconsider the applicability of processors for certain tasks. In particular, particularly noticeable changes have occurred in the segment of energy-efficient “U” processors. In the 8th generation, these are finally full-fledged 4-core “stones” with significantly better performance than its predecessors, while maintaining the same TDP value. Therefore, I don’t see the point in choosing something like i7 7500U, i5 7200U, etc.
The only argument that can influence the decision to prefer these particular CPUs is a significant discount on laptops with them on board. In other cases, the old Us have no chance against new processors.
I’ll say right away that this is an average classification that does not take into account financial costs or the need to choose one option or another. And overall performance depends not only on the processor. Even a powerful “stone” may not reveal its potential if a small amount of memory is installed, a budget one is used HDD, and at the same time programs that are “greedy” for hardware resources are used.
You may also be interested...

189 comments
Hi all!
I wanted to know about Intel processors. I have long noticed that when buying a newly released processor, the year is indicated on its cover, but the year does not correspond to the year of purchase, for example, the processor was presented in 2018, but the Intel processor is ’13.
Is this the year of development?Andrey, hello. help me choose a laptop for playing Dota 2. The amount is up to 70 thousand. Tomorrow I will go for a laptop, I still haven’t decided which one I want) I read a lot which one to get, etc. But since I don’t know much about this, it gave me almost nothing)) please help with advice, thanks in advance.
Hello. And I have this one on my desktop PC
asustek computer inc motherboard M4A785T-M (AM3)
amd phenom iix4 965 deneb 45nm technology. Is it possible to find a replacement motherboard?Good article, informative :)
But there is one remark and, subsequently, a question. The article does not contain a description of the T, K, S markings. There are also G-series Pentiums, but that doesn’t matter)
And the next one is about marking k. As far as I know, k means the unlocked multiplier, i.e. The processor can be overclocked, is that true?
Does k-multiplier have anything to do with Hyper-Threading technology?
I can’t understand why the i7-3770k has 4 cores and 8 threads, and the similar performance i5-3570k has 4 cores and 4 threads, although both are labeled k.Hello. I'm looking for a laptop to work with AutoCad 2016. Please help me with advice on which one to choose. There is a lot of information, but it’s impossible to put it all together. Thank you in advance.
Good afternoon. Super article. I have been interested for a long time and have a question... just about the letter M... I saw that you answered about mobility... but I would like to know whether the difference with U and HQ/HK is significant. What percentage, say, in terms of games and working with graphic editors?
Please tell me what is better: lenovo i5-7200U+mx130 8ram ddr4-2133 or acer i3-8130U+mx150 8ram ddr4-2133? Does it make sense to overpay for a more expensive Acer?
Hello, I have a laptop Acer Aspire 7750g intel core i5 2450M 2.50GHz + turbo boost I want to install an external video card via EXP GDC
does it make sense and what is the optimal video card to take for games thanksHello!
Are there any other questions…..
I found three interesting options with an i7 8750H with a GTX 1070...and one with an i7 7700HQ with a GTX 1080.
i7 7700HQ with GTX 1070 many options and lower price.
Generally stuck with the choice of Acer, Asus or Del. All very cool (in my opinion)…..in the same price niche.
With a cool card it's ASUS ROG GL702VI.....does it make sense?
Plus I found an option with an i7 7820HK processor (it seemed to be very popular before).
And how much operational intelligence is better for this matter?
I take it mainly for games... what do you recommend?
Until now I have used simpler technology. Muchooo.
It’s not possible to change often, I want to spare. Thank you.Good evening, thank you for providing some clarification on this topic, if it’s not too much trouble, can you recommend several gaming laptops in a budget of up to 45 thousand, I’ve looked at the HP 15-bs105ur 2PP24EA, but would like to hear your options.
Thank you in advance.Good afternoon Please tell me I need a laptop for programming. We are considering options like Aser swift 5 with 16 Gb of RAM and Intel Core i7 8550U. I know that ultrabooks limit the processor frequency to reduce overheating. Do you think this will greatly affect the operation of the laptop? Or is it better to consider heavier, but air-cooled laptop options?
Andrey, good evening. Thanks for the article, very informative. I would be grateful if you could clarify one point. I roughly narrowed the circle, taking into account my needs (diagonal 17, not for games, for AutoCAD 3D? budget up to 65tr) to ACER Aspire A717. But then I got confused in the modifications. There are two similar modifications with the only difference being the series. The first cheaper screen: 17.3″; screen resolution: 1920×1080; processor: Intel Core i5 7300HQ; frequency: 2.5 GHz (3.5 GHz, Turbo mode); memory: 8192 MB, DDR4; HDD: 1000 GB, 5400 rpm; SSD: 128 GB; nVidia GeForce GTX 1050 - 2048 MB second more expensive by 6tr (65tr) Intel Core i7 7700HQ; frequency: 2.8 GHz (3.8 GHz, Turbo mode); memory: 8192 MB, DDR4; HDD: 1000 GB, 5400 rpm; SSD: 128 GB; nVidia GeForce GTX 1050 - 2048 MB;
Is it worth overpaying for the series? and generally normal hardware for my requirements? I’m also puzzled by the fact that these prices are relevant, provided that the Linux operating system on Windows will be 7-10 thousand more expensive.Hello.
Linux is, consider it, without an operating system. They don't charge money for it. A licensed Windows- this is at least several thousand.
AutoCAD loves processors with higher frequencies. In general, the i7 is better, but there is one thing - cooling. It’s not a fact that the laptop will cope with cooling the i7 under prolonged load. I mean, he can handle it, but how much faster the i7 will work in this mode compared to the i5 is a question. And it would be better to have more memory. I would still put in 16 GB of memory. There's probably no need for more. Although you can upgrade it yourself later if necessary. SSD is a must. 240-256 GB would be better, 128 is still not enough. I think i5 will be enough.
Why a laptop? Wouldn't a hospital be better for such tasks? It’s easier to upgrade, and there are no problems with cooling.Thank you very much. The specifics of the work are such that a laptop is more convenient. with cooling, I’ll buy a stand so that I don’t have to worry)) you can buy it cheaper without an ssd, but you need everything back cover remove to add ssd? which is fraught with loss of warranty, and modifications with higher capacity come with more expensive components. There is a separate window for a regular hard drive, maybe you can put a hybrid hhd+ssd version there? It’s also very interesting how much worse or better is the 8th generation processor but with the U series (2 cores) than the 7th series processor with the HQ series?
The modification indicated on the box is NH.GTVER.006. I don’t see such an assembly at all on the manufacturer’s website. The city link doesn't say anything about the matrix, but the phone managers say it's ips. I looked in other stores, they also write ips. In any case, I will try to return or exchange, insisting that within 7 days I have the right by law and contract)
Hello, could you comment on this unit:
Dell Vostro 5568 (Intel i5-7200U 2500MHz / 8192MB / SSD 256GB / nVidia GeForce 940MX / gold)
Good day, Andrey!
I'm looking for advice on choosing a laptop.
Budget - up to 50-55. But if you can get it cheaper, then it’s much better.
The main goal is to connect to a 4K TV and be able to view content (video) in this format. The games are not relevant, but there will be an opportunity to play them (in 4K, or in FullHD) good addition. Working with documents, surfing.
Nominees:
1. Acer Aspire A715-71G-51J1 NX.GP8ER.008
2. ASUS FX553VD-DM1225T 90NB0DW4-M19860
3. Dell G3-3579 G315-7152 BlueKeep in mind that we will increase the HDD and SSD on our own, and we will install additional RAM in the future.
Thanks in advance!
PS From your publication and responses to comments, I found out that it is necessary to select a laptop without an OS. This significantly reduces its final cost.
Hello.
Please tell me. Choosing a laptop, worth it Asus models and MSI.
Which model would be preferable?
Main computing power and RAM. For example, for working with data programs.Hello. looking for gaming laptop V price category up to 70,000:
In stores they advise
— Asus VivoBook 15 K570UD
— Lenovo IdeaPad 330 Series 330-15ICH
Please rate and tell me which other models may be suitable. The company is preferable to Asus, but I won’t turn my nose up at others. I would like to choose the optimal selection of processor (i5 8300H/ i7 8550U/ i7 8750H and higher) and video card (GeForce® GTX 1050/ GeForce® GTX 1050 Ti and higher) + SSD. Screen 17 is preferable.
Thanks in advance.P.S. Is it true that the i5 8300H will discharge faster and overheat the laptop? Should I focus on it or the i7 line within my budget?
Good afternoon. Please recommend a laptop for: development (with IDE - no problem), photoshop, illustrator. It is advisable to have ssd + hdd (but you can also just have a hdd, with the possibility of adding an ssd), 8GB of RAM (more is possible). I'm confused about the options...
The previous one had a 2nd generation i5, 6 GB of RAM and an integrated + discrete video card. I want no worse, budget 50k.
Thank you!Hello Andrei! I understand that the article is about processors, but I see that you are also helping with choosing a laptop. I will make the same request. I've already broken my head - I've read a lot of information, watched videos... everything is mixed up.)) The laptop is needed for use at home, mainly for my daughter for studying, but sometimes my husband and I will use it - for him to make presentations, for me - for working with photos, watching movies . My daughter has vision problems - we are only considering a 17-inch screen with good resolution. We are not gamers - we do not plan to play tanks. Maybe if only for light games, and even then for children. Budget up to $1500. Well +\- $200. We are considering the companies Asus, Aser and Dell. We give preference to the latter. We are not considering HP, there are no arguments, we just don’t intuitively want to. I would also like a metal laptop. The weight doesn't bother me - we'll only use it at home. Please recommend several models that you think are suitable for our family. Thank you very much in advance!
Hello.
I'm looking for a laptop for work. I do accounting and look at the screen a lot. Budget about $850. I wanted to choose a laptop with a good 15.6-inch screen and the ability to sometimes play games (at medium and low settings, but modern games). Of all the models for this money I liked Acer laptop Aspire 7 A715-72G-513X NH.GXBEU.010 Black and Laptop Lenovo IdeaPad 330—5ICH 81FK00FMRA Onyx Black (https://ktc.ua/goods/noutbuk_lenovo_ideapad_330_15ich_81fk00fmra_onyx_black.html, https://ktc.ua/goods/n outbuk_acer_aspire_7_a715_72g_513x_nh_gxbeu_010_black. html). The filling seems to be the same. I can not decide. Help me make a choice. Maybe I missed something? Maybe there is a more interesting model? I'll install the OS myself. Can an SSD be delivered to any laptop or does it require a special connector?Hello! Could you please advise reliable laptop in the area up to 40,000. Needed for watching movies, listening to music, Internet. I don’t play games. I previously looked at the HP 15-bw065ur 2BT82EA laptop, but it’s very confusing that there’s not much information about this company good feedback. (cooling problem). Now I’m looking at the ASUS R542UF-DM536T laptop. But what’s confusing about it now is that it has a 2.2 GHz Core i3-8130U processor. As I understand it, if the letter is U, then you shouldn’t take it. In general, I'm confused about the characteristics and don't know which one to choose. Please advise.
Hello from Kyrgyzstan, and I would like to know if I have a choice between i5 8265U with 8 GB RAM, mx130 video card with 4 GB and i5 7300HQ with 8 GB RAM, GTX video card 1050 Ti. What to choose (the purpose of the purchase is programming and maybe in the future toys to play with), given that the second option is sold used? The price of the first is 43.5k, and the second is sold for 45k soms (at the rate of som and rubles almost 1 to 1). I will be grateful for your answer)
Good afternoon!
Please advise on budget random access memory.
I bought a laptop with 4GB RAM soldered on board. I checked the availability of a free slot for an additional bracket.
In terms of volume and frequency, I will buy additional DDR4 2133 8GB.
A search found the following brands:
1. Apacer
2. Goodram
3. FoxlineWhich manufacturer? is it better to give preference? The price for all is around 3300-3700 rubles. Or maybe there are other manufacturers?
Thanks in advance!Hello. Tell me which laptop to choose for working and watching movies. I need something that’s not expensive, so far I’ve looked at two options: ASUS laptop F540BA-GQ193T (AMD A6 2.6GHz/15.6”/1366x768/4GB/500GB HDD/AMD Radeon R4/DVD no/Wi-Fi/Bluetooth/Win10 Home x64) and Lenovo IdeaPad 330-15AST (81D600FQRU) (AMD A4- 9125 2.3GHz/15.6”/1366x768/4GB/500GB HDD/AMD Radeon 530/DVD no/Wi-Fi/Bluetooth/Win10 Home x64). And also, what is the difference in two almost identical laptop models, but only different letters: Lenovo IdeaPad 330-15AST (81D6002GRU) and Lenovo IdeaPad 330-15AST Laptop (81D600FQRU). Designation in brackets. Info from the websites of two well-known retail chains. I would really appreciate your answer. Thank you.
The next 3 digits are the serial number of the model. In general, the higher the value, the more powerful the processor. So, i3 has a value of 7100, I5 – 7200, i7 is marked as 750; what does this mean? Why are the 7th generation processors listed?
Let's figure out what the main differences are between the processors of the world leaders - Intel and AMD.
We will also consider their positive and negative sides.
Major CPU Manufacturers
Everyone understands perfectly well that the market computer technology There are two leading companies that are engaged in the development and production of the Central Processing Unit (central processing unit), or, more simply put, processors.

These devices combine millions of transistors and other logic elements, and are electronic devices of the highest complexity.
The whole world uses computers whose heart is an electronic chip from either Intel or AMD, so it’s no secret that both of these companies are constantly fighting for leadership in this area.
But let's leave these companies alone and move on to to the average user, who is faced with a dilemma of choice - what is still preferable - Intel or AMD?
Whatever you say, there is not and cannot be a definite answer to this question, since both manufacturers have enormous potential, and their CPUs are capable of meeting the current requirements.
When choosing a processor for your device, the user primarily focuses on its performance and cost - relying on these two criteria as the main ones.
The majority of users have long been divided into two opposing camps, becoming ardent supporters products from Intel or AMD.
Let's look at all the weak and strengths devices of these leading companies, so that when choosing a particular one, rely not on speculation, but on specific facts and characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of Intel processors

So, what are the advantages of Intel processors?
- First of all, this is very high performance and speed in applications and games, which are most optimized for Intel processors.
- Under the control of these processors, the system operates with maximum stability.
- It is worth noting that the second and third level memory of the CPU Intel work no more high speeds than in similar processors from AMD.
- Multithreading, which is implemented by Intel in CPUs such as Core i7, plays a big role in performance when working with optimized applications.
Advantages and disadvantages of AMD processors

- The advantages of AMD processors include, first of all, their affordability in terms of cost, which is perfectly combined with performance.
- A huge advantage is the multi-platform, which allows you to replace one processor model with another without the need to change the motherboard.
- That is, a processor designed for socket AM3 can be installed on socket AM2+ without any negative consequences.
- One cannot fail to note multitasking, which many AMD processors cope well with, simultaneously running three applications.
- In addition, FX series processors have quite good overclocking potential, which is sometimes extremely necessary.
- The disadvantages of AMD CPUs include higher power consumption than Intel, as well as operation at more low speeds memory cache of the second and third levels.
- It should also be noted that most processors belonging to the FX line require additional cooling, which will have to be purchased separately.
- And another disadvantage is that under AMD processor Fewer games and applications have been adapted and written than for Intel.
Current connectors from Intel
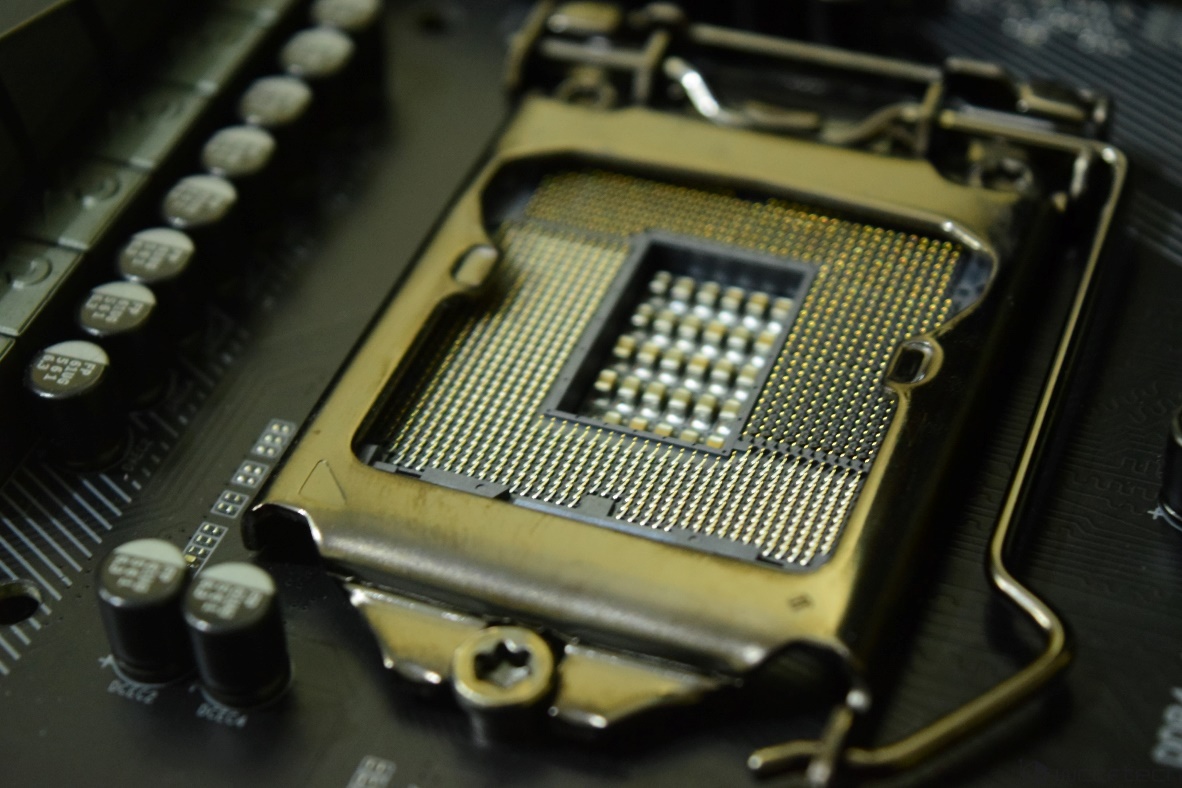
Today many leading manufacturers central processing units equipped with two current connectors. From Intel they are as follows:
- LGA 2011 v3 is a combined connector that is focused on the rapid assembly of high-performance personal computer both for servers and for the end user. The key feature of such a platform is the presence of a RAM controller that successfully operates in multi-channel mode. Thanks to this important feature, PCs with such processors are characterized by unprecedented performance. It must be said that within the framework of such a platform an integrated subsystem is not used. Unlocking the potential of such chips is only possible with the help of discrete graphics. To do this, you should use only the best video cards;
- thanks to LGA, you can easily organize not only high-performance computer system, but also a budget PC. For example, a socket LGA 1151 perfect for creating a medium-sized computing station pricing policy, at the same time will have a powerful built-in graphics core Intel Graphics series and support DDR4 memory.
Current AMD connectors

Today AMD is promoting the following processor sockets:
- The main computing platform for such a developer is considered AM3+. The most productive CPUs are considered the lineup FX, which includes up to eight computing modules. In addition, such a platform supports an integrated graphics subsystem. However, here the graphics core is included in the motherboard, and is not integrated into the semiconductor crystals;
- the latest modern AMD processor socket – FM3+. AMD's new CPUs are intended to be used in desktop computers and media centers not only at entry-level, but also at mid-level. Thanks to this, the most modern integrated solution will be available to the average user for a fairly small amount.
Working possibilities

Many people first pay attention to the price of the processor. It is also important for them that he can easily solve the tasks assigned to him.
So, what can both organizations offer on this point? AMD is not known for outstanding achievements.
But this processor represents an excellent price-performance ratio. If configured correctly, you can expect stable work no complaints.
It is worth noting that AMD managed to implement multitasking. Thanks to such a processor, various applications can be easily launched.
With its help, you can simultaneously install the game and surf the vast expanses of the Internet.
But Intel is known for more modest results in this area, which is confirmed by the comparison of processors.
It would not be superfluous to pay attention to the availability of overclocking, during which the performance of an AMD processor can easily be increased by twenty percent compared to standard settings.
To do this, you just need to use additional software.
Intel beats AMD in almost everything except multitasking. In addition, Intel is working with
So you should select the motherboard and power supply much more carefully to prevent freezes due to insufficient power.
Power consumption chart for Intel and AMD It's the same story with heat dissipation. It is quite high in older models. As a result, a standard cooler has difficulty coping with increased cooling.
Therefore, when purchasing a CPU from AMD, you must additionally purchase high-quality cooling from any decent company. Don't forget that high-quality fans make much less noise.
Socket type and performance

We should also say something about performance. After AMD acquired ATI, its creators managed to successfully integrate most graphic capabilities processing in the processor cores. Such efforts have paid off successfully.
Those who use an AMD chip for gaming should have no doubt that they get good performance, which is much more better indicators equivalent chips from Intel (this is especially true for those who use a card with ATI graphics).
If it comes to heavy multitasking, then it is better to choose Intel, since it has HyperTreasing technology.
However, this advantage can only be used when software application capable of supporting multitasking, that is, the ability to divide tasks into several small parts.
If the user needs gaming processor, it is better to combine an AMD processor with a video card.
So, there is a big difference between intel and amd processor sockets. When choosing the right option, consider the differences between them listed in this article. This will make choosing the right option much easier.
