Summary from Access database. What is the difference between Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Access?
The two Microsoft Office products – Access and Excel – often seem almost identical to the user. This representation consists of a tabular method of organizing data. Both Access and Excel work with tables, are capable of processing and analyzing data, and performing complex calculations. In order to solve the assigned tasks with minimal time and labor, it is worth determining which program is more suitable for this.
Concept of Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Access
Microsoft Excel– a program for working with data tables created by by Microsoft and included in the pact Microsoft programs Office.
Microsoft Access – relational system database management included in Microsoft package Office.
Comparison of Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Access
As we can see from the definitions, the key difference between Access and Excel is in the subject of action: Excel works with spreadsheets, Access – with databases in a table view. Externally it looks very similar. IN Excel data are stored in cells that form columns and rows, combined into sheets. In Access, data is stored in tables that together form a database. A sequence of data in one row is called a record in Access.
Excel performs the task of organizing data within a single table, Access performs complex queries data, referring to a set of tables. Therefore, an Excel table is a non-relational collection of data, and Access is a relational one, in which each specific object has connections in other tables. In Excel, each table cell has a unique identifier made up of the row number and column letter; in Access, the record is equipped with a unique identification key.
Access is advisable to use if the data array is very large and the relationships between them are complex. In this case, the interaction of tables within relational base data will be provided fast control. Excel is suited to the tasks of calculations and statistical comparisons of small amounts of data. If the data is predominantly numeric, then it is more convenient to work with Excel, but if there are a lot of them text values– Access.
If multi-user work is expected with the database, and constant and multiple modifications are required, then Access will not have any problems in solving such problems. Excel is designed for a single user and has relatively static content.
Difference between Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Access
1. Excel works with data tables, Access works with tabular databases.
2. Perform more complex queries in Access.
3. Excel is a non-relational collection of data, Access is relational.
4. Excel's unique identifier depends on the names of columns and rows; in Access, the identification key is autonomous.
5. Access is designed to work with large amounts of data.
6. Excel works primarily with numeric data.
7. Multi-user work is available in Access.
Microsoft Objects Access
Microsoft Access calls anything that can have a name (in the Access sense) objects. In an Access database, the main objects are tables, queries, forms, reports, macros, and modules. In other DBMSs, as a rule, the term database usually refers only to the files in which the data is stored. In Microsoft Access, the database includes all objects associated with stored data, including those that are defined to automate work with them. Below is a list of the main Access database objects.
1. Table. An object that is defined and used to store data. Each table includes information about a specific type of object, such as customers. The table contains fields (columns) that store various types of data, such as the client's last name or address, and records (also called rows). The record contains all the information about a certain object (person, product sample, etc.). For each table you can define primary key(one or more fields containing values unique to each record) and one or more indexes that help speed up data access. This object in the database is the main one.
2. Request. An object that allows the user to retrieve the desired data from one or more tables. You can use a QBE (Query Based Query) form or SQL (Structured Query Language) statements to create a query. You can create queries to select, update, delete, or add data. You can also use queries to create new tables using data from one or more existing tables.
3. Form. An object primarily intended for entering data, displaying it on the screen, or controlling the operation of an application. Forms are used to implement user requirements for presenting data from queries or tables. The forms can also be printed. Using a form, you can run a macro or VBA procedure in response to some event, such as a change in the value of certain data.
4. Report. An object used to create a document that can later be printed or included in a document in another application.
5. Macro. An object that represents a structured description of one or more actions that Access should take in response to a specific event. For example, you can define a macro that, in response to selecting an element on the main form, opens another form. Using another macro, you can check the value of a certain field when its contents change. You can include in a macro additional conditions to perform or not perform certain actions specified therein. You can also run another macro or VBA procedure from one macro.
6. Module. An object containing programs written in a language Visual Basic for applications. Modules can be independent objects containing functions that can be called from anywhere in the application, but they can also be directly “tied” to individual forms or reports to react to certain changes that occur in them.
7. Access pages. Pages – serve to provide access to data contained in a database remote from the consumer (for example, via the Internet).
The conceptual relationships of Access objects are shown in Figure. 2.
Rice. 2 Relationships between basic objects in Microsoft Access
Database fields and records
In a database, everything is presented in the form of tables, so a field is a column and a record is a row. A field is the simplest database object designed to store parameter values real object or process. The field can be characterized the following parameters: name, data format, design type.
A database record is a table row containing a set of property values located in database fields.
At first glance, the Access DBMS is very similar to an electronic program Microsoft tables Excel according to its purpose and capabilities. However, there are fundamental differences between them:
- When working with an Excel spreadsheet, you can enter any information into a table cell, so you can place a table, text, and a drawing on the worksheet. If necessary, different data can be entered in one column of the table - numbers, text, dates. A table in an Access database differs from a table in Excel in that, as mentioned above, a data type is defined for each record field, i.e., you cannot enter data of different types in one column of the table in different rows.
- Access allows you not only to enter data into tables, but also to control the correctness of the entered data. To do this, you can set validation rules directly at the table level. Then, no matter how the data is entered - directly into a table, in a form, or on a data access page, Access will not allow you to save data in a record that does not meet the specified rules.
- It is convenient to work with Excel tables if they contain limited number rows, database tables may contain great amount records, and at the same time the DBMS provides convenient ways extracting the necessary information from this set.
- If you store all the data necessary for work in Word documents and spreadsheets, as information accumulates, you may simply become confused large quantities files, Access allows you to store all data in one file and access to this data is carried out page by page, i.e. limits on computer memory resources are not exceeded.
- Access allows you to create relationships between tables, allowing you to share data from different tables. In this case, for the user they will be presented as one table. Implementing such a feature in spreadsheet management systems is difficult, and sometimes simply impossible.
- By establishing relationships between individual tables, Access allows you to avoid unnecessary duplication of data, save computer memory, and increase the speed and accuracy of information processing. This is why tables containing duplicate data are split into several related tables.
- Excel allows multiple users to work with one document, but these capabilities are very limited; Access can support 50 users working simultaneously with the database, while all users are guaranteed to work with up-to-date data.
- Access has a developed system of protection against unauthorized access, which allows each user or category to see and change only those objects to which he has been granted rights by the system administrator, for example, you can prohibit the use of certain menu commands, opening certain forms, changing data in tables or forms. Spreadsheets also allow you to password-protect your data or enable view-only data, but these tools are much simpler.
Thus, we can say that the Access DBMS is used in cases where an application task requires storing and processing heterogeneous information about a large number of objects and assumes the possibility of a multi-user operating mode. An example would be the task of maintaining warehouse accounting. Electronic Excel tables are convenient means storage limited quantity tabular data with extensive capabilities for performing calculations and data analysis. Excel Documents Intended, as a rule, for individual use.
Excel's capabilities are of course not limited only to spreadsheets; for example, Excel can be very successfully used to analyze data that is stored on a database server (in particular, in Microsoft SQL Server), but in this case Excel is not a data warehouse, but only provides data processing.
Modern civilization is in dire need of constant processing and preservation large volumes various data. There is also a constant need to monitor the impact of their changes on other information arrays. It is most convenient to organize all these processes in the form of a database. A convenient tool for such an organization it may become popular program Access DBMS.
What is a DBMS
Various data are usually presented and stored in the form of tables. It often happens that several tables contain information that is related to each other in some way. The collection of such interdependent tables constitutes a database.
In order to be able to fully operate with data from the database, it is also necessary to execute queries. And in order to facilitate filling out the database with initial information, specially designed forms are usually used. To automate the process, in some cases it is necessary to additionally use macros. The combination of additional tools forms a system called DBMS - database management system. An example would be Foxpro, Oracle, Microsoft Access DBMS.
Basic functions of the DBMS
The Access DBMS performs the following important functions:
Implementation of necessary formulas;
Establishing connections between tables and data sets;
Ability to add requests.
The whole set tools, which is available in the DBMS arsenal, is intended to fully service two main areas during operation information system. This is the organization of design and modification of the structure and various necessary data manipulations.

Main differences of the Access DBMS
From many others that are used by programmers to automate work with databases, the Access DBMS is easy to learn. Because the this platform Russified, and also has a standard for all MS programs Office interface, even inexperienced users will not feel any inconvenience while mastering it.
At the same time, Access is a full-fledged program management of data arrays with all the necessary attributes. The created system can be used not only on a separate computer, but also in an extensive local network.
Access features

This program makes it possible to create source objects in the form of tables with fields of various types, for example, numeric, text, graphic, even OLE fields.
Moreover, communication between tables is ensured, while cascading data updates and cascading deletes are supported if necessary.
All basic operations with data are performed, such as entering, viewing, storing, updating, sorting, filtering, and obtaining selections. Indexing by selected fields and control of entered information is also carried out.
When filling out fields, calculations using various formulas can be used.
Access DBMS is a convenient and understandable program that has all the capabilities of similar professional applications.
At first glance, the Access DBMS is very similar in its purpose and capabilities to the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet program. However, there are fundamental differences between them.
- When working with an Excel spreadsheet, you can enter any information into a table cell, as a result of which you can place a table, text, and a drawing on the worksheet. If necessary, different data can be entered into one column of the table - numbers, text, dates. A table in an Access database differs from an Excel table in that, as mentioned above, a data type is defined for each record field, i.e., you cannot enter data of different types in one column of the table in different rows.
- Access allows you not only to enter data into tables, but also to control the correctness of the entered data. To do this, you need to set validation rules directly at the table level. Then, no matter how the data is entered - directly into the table, through screen form or on the data access page, Access will not allow you to save data in a record that does not meet the specified rules.
- Excel tables are convenient to work with if they contain a limited number of rows. Database tables can contain a huge number of records, and the DBMS provides convenient ways to extract the necessary information from this set.
- If you store all the data you need for work in Word documents and spreadsheets, then as information accumulates, you may simply get confused in a large number of files. Access allows you to store all your data in one file and access this data page by page, that is, without exceeding the limits on your computer's memory resources.
- Access allows you to create relationships between tables, allowing you to share data from different tables. In this case, for the user they will be presented as one table. Implementing such a feature in spreadsheet management systems is difficult, and sometimes simply impossible.
- By establishing relationships between individual tables, Access allows you to avoid unnecessary duplication of data, save computer memory, and increase the speed and accuracy of information processing. To do this, tables containing duplicate data are divided into several related tables.
- Excel allows multiple users to work on the same document, but these capabilities are very limited. Access can support 50 simultaneous users working with the database, and all users are guaranteed to work with up-to-date data.
- Access has a developed system of protection against unauthorized access, which allows each user or group of users to see and change only those objects to which he has been granted rights by the system administrator, for example, you can prohibit the use of certain menu commands, opening of certain forms, changing data in tables or forms. Spreadsheets also allow you to password-protect your data or enable view-only data, but these tools are much simpler.
Thus, the Access DBMS is used in cases where the application task requires storing and processing heterogeneous information about a large number of objects and assumes the possibility of multi-user mode. An example would be the task of maintaining warehouse records. Excel spreadsheets are a convenient means of storing a limited amount of tabular data with extensive capabilities for performing calculations and analyzing data. Excel documents are generally intended for individual use.
Comment
Excel's capabilities, of course, are not limited only to spreadsheets; for example, Excel is very convenient to use for analyzing data that is stored on a database server (in particular, Microsoft SQL Server), but in this case Excel is not a data warehouse, but only provides data processing.
Working with VB project (12)
Conditional Formatting (5)
Lists and ranges (5)
Macros (VBA procedures) (63)
Miscellaneous (39)
Excel bugs and glitches (3)
Summary from Access database
Let's assume you have a large database. Let's call it "products". And by large I mean about 3 million records (rows) or more. Directly to one Excel sheet This amount of data will definitely not fit. You can, of course, store it on different sheets. Then you can use the article Pivot table from multiple sheets. But first of all, this method does not work very stable and may require changes depending on Excel versions and also requires permission to execute macros, and secondly, for such a number of records this is not The best decision, because storing so much data in Excel workbooks is not entirely correct. Therefore, even if you have several books/sheets filled with the necessary data in full and you need to combine this data for further analysis using a pivot table, the best solution in my opinion is to combine them through MS Access into one table and then build a pivot table based on the table will not be difficult.
Creating a database in Access from several ranges
In order to correctly and painlessly collect data from several tables from Excel into Access, you need to prepare these tables. Which isn't that difficult. To do this, you must follow the following rules:
- all tables must contain the same number of columns with completely identical headers
- headings should not contain line breaks, dashes, hyphens, periods, or commas. It’s better to completely abandon any punctuation marks and dubious symbols - leave only spaces between words (and even then it’s better to replace them with underscores)
- if the tables contain numeric data that will subsequently need to be summarized, make sure that all the data is numeric and not textual. This will help avoid import errors
- you need to make sure that the tables do not contain empty rows and columns, as well as merged cells
Now that all the tables are ready, you can start importing data into Access. Open Access and select Create (New) - New base data (Blank database). Specify the name of the database and location (folder):
After creating the database, we go through several steps:

The first part of the base is full. Now you need to supplement the table created in Access with data from other sheets or workbooks. To do this, we repeat all the steps described above, but in the 2nd step we select Append a copy of the record to the table. Then the data will be added to the table we have already created from the first sheet, and will not be written to a new one (which we don’t need).
That's it, now you can start creating a pivot table.
Create a pivot from an Access database
Before creating a summary based on external sources, you must add to the panel quick access button that will allow you to do this:
- Excel 2010- File- Options-
- Excel 2007- Office button- Excel Options(Excel options)- Quick Access Toolbar
or directly from the Quick Access Toolbar: 
Select commands from: All Commands. We are looking there PivotTable and PivotChart Wizard and transfer it to the quick access panel: 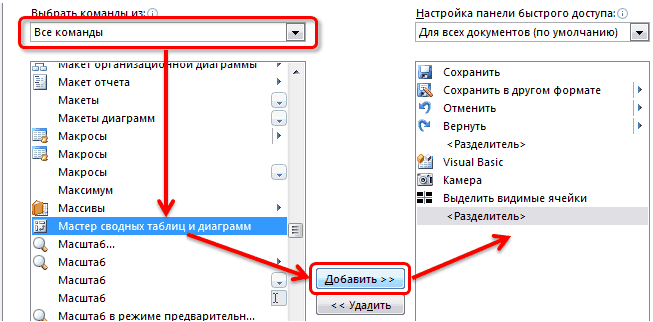
Now click on this button and in the first step of the Wizard window that appears, select in external source data (external data source):
in the second step press the button Get Data:
In the window that appears, you must select MS Access Database or MS Access Database.
There is important point. Check mark Use the Query Wizard to create/edit queries must be enabled. Click OK.
Next, select in the right window the folder in which our database is located. In the left window, select the Database file itself: 
Confirm your choice by pressing the button OK.
Next, you need to create a selection query. Essentially, you can simply click on the name of the Database table and then on the “>” icon 
But if you need to work only with some columns from the entire table, you can sequentially move them to the right field (after expanding the plus sign next to the table name in the left field). You can remove unnecessary columns from the right field by clicking the "Next" button. In the next window you will be asked to make a selection based on the conditions (rules): 
If you don’t really understand what it is and you don’t need it (and in in this case you really don’t need it) - just skip this step and click again Further.
We also skip this step (sorting) - it is completely useless to us, because... We will still process the data aggregated. So we press again Further. And the final step of the query wizard: 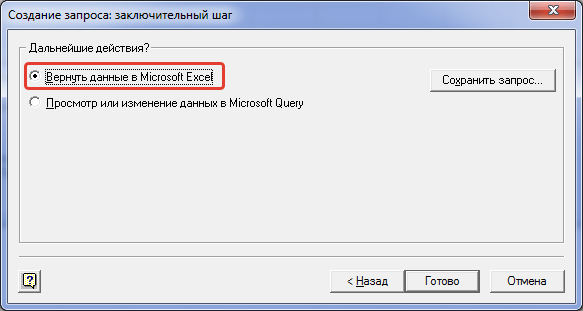
choose Return Data to Microsoft Excel and click Ready. At the same time, in the window of the second step of the Pivot Tables and Charts Wizard to the right of the button To get data the inscription should appear Data fields have been retrieved:
If you see this inscription, then feel free to click Next and on last step wizard, select the cell and sheet in which you want to place the pivot table: 
Either to an existing sheet (you will have to specify the cell in which the first row of data will be placed), or to a new sheet.
Click Finish.
That's it, our summary is ready to work and now you can process your millions of records quickly and easily in the familiar interface of the summary itself.
("Bottom bar":("textstyle":"static","textpositionstatic":"bottom","textautohide":true,"textpositionmarginstatic":0,"textpositiondynamic":"bottomleft","textpositionmarginleft":24," textpositionmarginright":24,"textpositionmargintop":24,"textpositionmarginbottom":24,"texteffect":"slide","texteffecteasing":"easeOutCubic","texteffectduration":600,"texteffectslidedirection":"left","texteffectslidedistance" :30,"texteffectdelay":500,"texteffectseparate":false,"texteffect1":"slide","texteffectslidedirection1":"right","texteffectslidedistance1":120,"texteffecteasing1":"easeOutCubic","texteffectduration1":600 ,"texteffectdelay1":1000,"texteffect2":"slide","texteffectslidedirection2":"right","texteffectslidedistance2":120,"texteffecteasing2":"easeOutCubic","texteffectduration2":600,"texteffectdelay2":1500," textcss":"display:block; padding:12px; text-align:left;","textbgcss":"display:block; position:absolute; top:0px; left:0px; width:100%; height:100% ; background-color:#333333; opacity:0.6; filter:alpha(opacity=60);","titlecss":"display:block; position:relative; font:bold 14px \"Lucida Sans Unicode\",\"Lucida Grande\",sans-serif,Arial; color:#fff;","descriptioncss":"display:block; position:relative; font:12px \"Lucida Sans Unicode\",\"Lucida Grande\",sans-serif,Arial; color:#fff; margin-top:8px;","buttoncss":"display:block; position:relative; margin-top:8px;","texteffectresponsive":true,"texteffectresponsivesize":640,"titlecssresponsive":"font-size:12px;","descriptioncssresponsive":"display:none !important;","buttoncssresponsive": "","addgooglefonts":false,"googlefonts":"","textleftrightpercentforstatic":40))
