Smartphone with atmospheric pressure sensor. Sensors in smartphones: what are they? Is there a device in the smartphone?
Availability of many sensors in modern mobile devices, this is a known fact, but how many there are and what these sensors are used for is a mystery. Many manufacturers indicate only the main well-known sensors in phones, like accelerometer, gyroscope And proximity sensor. But the vast majority of manufacturers write little at all about the sensors used and other electronics that their device is stuffed with.
We decided to clarify the situation with smartphone and tablet sensors. The purpose of the article is to tell what types of sensors there are, what they serve, in what devices they can be found and how.
Sensors are various devices that read additional information. These solutions make working with a phone, tablet or other gadget more convenient and add functionality to the device.
The presence of many sensors in modern mobile devices is a known fact, but how many there are and what these sensors are used for is a mystery. Many manufacturers list only the basic well-known sensors, such as the accelerometer, gyroscope and proximity sensor. But the vast majority of manufacturers write little at all about the sensors used and other electronics that their device is stuffed with.
We decided to clarify the situation with smartphone and tablet sensors. The purpose of the article is to tell what types of sensors there are, what they serve, in what devices they can be found and how.
Basic sensors in smartphones and tablets
Accelerometer
(accelerometer, orientation sensor, acceleration sensor)– the simplest sensor that can be found in any smartphone or tablet. It is mainly used to register the rotation of the smartphone from portrait to landscape orientation. Often, the accelerometer is called G-Sensor. In general, the accelerometer records the difference between the acceleration of an object and gravitational acceleration along three axes. The electronics then calculate the difference, draw conclusions and send a signal to the software - when and in which direction to turn the screen. This leads to the main disadvantage of the accelerometer - if there is no acceleration or it is not great, then the accelerometer stops registering the position of the device in space or does so with a large error. This negatively affects the accuracy of device control, for example, in games or when controlling a quadcopter. This is where the next sensor comes to the rescue.
Gyroscope
(gyroscope)– also serves to register the position of the device in space, but, unlike the accelerometer, it can record the angle of inclination along three axes of even a stationary device. Using a gyroscope in games increases accuracy, since developers will have access to information about the deviation of the device in degrees with an error of only 1-2 degrees. Many people believe that even inexpensive smartphones and tablets are equipped with a gyroscope. However, our experiment showed that inexpensive smartphones and tablets cannot boast of having a gyroscope - only an accelerometer. Here are a few smartphones and tablets where the gyroscope could not be detected:We also did not find a gyroscope in
And here is where the notorious sensor is:
We also discovered a gyroscope in,. And there is no doubt that a gyroscope and a solid set of other sensors are contained in TOP solutions like, and other best modern smartphones.
Surprisingly, in the LG G4S and Asus FonePad 8 (which we already wrote about -) the gyroscope is not visible in the list of sensors, but there are plenty of auxiliary sensors:
In fairness, it should be noted that the auxiliary sensors, which we discussed at the very end of the article, can offset the absence of a gyroscopic sensor, but, we believe, not completely.
Geomagnetic sensor
(geomagnetic field sensor, magnetometer)– a sensor that responds to the earth’s magnetic fields. It can be used to determine the cardinal directions, which is why it is often called an electronic compass. In particular, the presence of such a sensor will greatly help devices without a GPS module determine their location (with the help of WiFi and cell towers, of course). The magnetometer is one of the key sensors, which, together with the accelerometer and gyroscope, allows developers to use the device to its full potential. Sometimes, to further improve accuracy, additional hardware sensors with similar but simplified functionality are added, such as the Geomagnetic Rotation vector sensor. Naturally, the magnetometer can be used for its intended purpose: as a metal detector, to search for wiring in walls, as a compass - look for what you need in app stores.
Some smartphone apps that use a geomagnetic sensor
Proximity sensor
(proximity sensor)– the sensor allows you to determine the object in front of you and the distance to it. It is an infrared emitter and receiver. When no radiation arrives at the receiver, there is no object, and when it does, the object from which the beam is reflected exists. This sensor makes it possible to turn off the display when you bring your ear close to the smartphone to make a call. Advanced versions of the sensor are used as a gesture sensor - the smartphone can recognize certain hand gestures and perform a given action. In some cases, a proximity sensor can be used to turn off the display when using a case (a cheap alternative to a Hall sensor).Light sensor
(light sensor, light sensor)– allows you to calculate the level of external illumination. A smartphone or tablet with a light sensor can independently increase or decrease the brightness level of the screen backlight, which is very convenient, since adjusting the brightness several times a day is not the most pleasant experience. In TOP smartphones and tablets, an advanced version of the light sensor can be used - an RGB sensor, which is capable of capturing the intensity of primary colors (red, green and blue) to further adjust the picture on the display or to adjust the balance for photography. Such a sensor can be found in the Galaxy Note 3, for example. And in Galaxy Note 4, the functionality of the light sensor has expanded to measure not only in the visible range, but also in ultraviolet. This ultraviolet sensor can measure the level of radiation and determine the time of day suitable for tanning.
Conclusion on the main sensors
So, if a smartphone or tablet has only an accelerometer, it means that this device is in the lowest price range and can only “rotate the screen.” This is the lot of cheap smartphones and tablets. Of course, there is a possibility that the manufacturer did not provide sane information about the types of sensors used - in this case, you need to start reading reviews that study in detail the hardware of the device using the System Info for Android application, for example.
The presence of an accelerometer, geomagnetic sensor, proximity and light sensor on a smartphone indicates that it is sufficiently equipped, but it is still not very good for controlling a quadcopter or games where tilt/rotate control is assigned to the user moving the smartphone. A gyroscope solves this problem - devices with a gyroscope accurately track the slightest deviations.
The presence of all of the above sensors, a large set of auxiliary sensors (discussed at the end of the article) and most of the sensors listed below indicate that this is an advanced device, the use of which will be a pleasure, and its capabilities will exceed all your expectations - these are the best tablets and smartphones.
Sensors in expensive smartphones and tablets
Hall Sensor
(Hall sensor)– picks up a magnetic field, like a magnetometer, but has a simple principle of operation, that is, it reacts only to field enhancements, and does not register tension along the axes. Used for using Smart Cover type covers - allows you to turn off the screen when the magnet built into the cover approaches it. This sensor is rarely indicated by manufacturers, so pay attention to the available accessories for a smartphone or tablet - if there is a “smart case” among them, then a Hall sensor is present.
Barometer
(pressure sensor)– a sensor that measures atmospheric pressure. It can be used both for its intended purpose and as an assistant to GPS/GLONASS modules to speed up the determination of the device’s location and altitude above sea level (altimeter).
Thermometer
(ambient temperature sensor)– ambient temperature sensor. It first appeared on the Galaxy S4 to improve the performance of the S-Health application, but is now used in many other expensive smartphones.Humidity sensor
(hygrometer)– also first appeared in the Galaxy S4 as an extension of the S-Health functionality.
Pedometer
(pedometer, step detector)– the self-explanatory name of the sensor hints that it determines whether a person has stepped or not. This is truly a separate sensor that allows you to more accurately detect steps and reduce the load on the accelerometer, which is the pedometer in most smartphones without a dedicated sensor. To help the pedometer, a Step Counter sensor and even a pedestrian activity motion sensor are sometimes added - a step counter and a pedestrian activity sensor (probably estimates the pace of walking). Such a sensor is found, for example, in the LG Nexus 5 and Galaxy Note 3.
Fingerprint's scanner
(fingerprint sensor, Touch ID)– a sensor that reads a unique fingerprint pattern. It’s strange to see a fingerprint scanner in an article about sensors - it would be better to include it in the section of an article about ensuring device security. However, this sensor can rightfully be considered one of the most important sensors in a modern smartphone. With its help, you can not only secure your smartphone, but also use it to open certain applications or confirm a payment.
Retinal scanner
(retina scanner)– a unique retina reader, this is the first place on the security pedestal. Such a sensor has been around for a long time, but its practical implementation in smartphones or tablets has not yet been noticed.
Heart rate sensor
(pulse meter, heart rate monitor)– first appeared in the Galaxy S5 so that the smartphone finally became a full-fledged personal trainer. The S-Health application began to receive more data about a person before, during and after training and was able to provide more accurate personal recommendations.

Dosimeter
- determines the dose of ionizing radiation or its power. In other words, the radioactive background can be measured. We have not seen a device with a built-in dosimeter in real life, but they say that in Japan there is a Pantone 5 smartphone equipped with this sensor. We're not surprised.
Auxiliary sensors that can be found in many smartphones and tablets
Sometimes, to further improve accuracy, additional hardware sensors with similar but simplified functionality are added (you may have seen them in the screenshots above).
Surely there are other sensors, but the secrets of their use are still known only to developers of operating systems and other software.
A modern smartphone is a complex high-tech computing device that is more powerful than thousands of on-board computers that launched the Apollo missions to the Moon half a century ago. There are also almost more sensors installed on board flagship mobile phones than on board this very Apollo. Each of them quietly but conscientiously performs their work. What do all these smartphone sensors do and how do they work? Read on for more details.
The light sensor in a smartphone is located on the front panel, usually near the earpiece (there are exceptions). Structurally, it is a semiconductor sensor sensitive to photon flux. Depending on its intensity, the sensor controls the display backlight in order to use battery power more efficiently. It can also perform an auxiliary function for other tasks by working with a proximity sensor.
Proximity sensor
This is an optical or ultrasonic sensor that determines whether there are objects in front of the screen. It sends a very weak light or sound pulse, and if it is reflected, it registers the reflected signal. Due to this, the screen is automatically locked during a call or when the smartphone is turned over with the display down. Traditionally, the proximity sensor is calibrated in such a way that it registers only 2 states: “a foreign object is closer than N (usually 5) centimeters” and “a foreign object is further than N cm”.
Accelerometer
This smartphone sensor is located on a circuit board and is a miniature electromechanical device that records the slightest movements. The responsibilities of this sensor include switching the orientation of the smartphone screen when tilted, controlling games, registering special control gestures (such as shaking or tapping the body), and also measuring steps (by counting rhythmic vibrations during walking).

A regular dual-axis accelerometer in a smartphone
There are two-axis and three-axis accelerometers. A feature of the accelerometer is that at rest, one of the axes will always show a value in the region of 9-10 m/s 2 (in a three-axis three-dimensional accelerometer). This is due to the fact that the Earth's gravity is on average 9.8 m/s 2 .
Gyroscope
The gyroscope is responsible for determining the movement and orientation of the smartphone in space. It also structurally represents a MEMS (microelectromechanical circuit) located on the system board. Its areas of application overlap with those of the accelerometer. The main differences are that the gyroscope has noticeably greater accuracy and measures movement not in m/s 2, but in radians or degrees per second. Due to this, it can be used to track head turns in a VR headset, as well as more accurately implement gesture control.

MEMS gyroscope under a microscope
Magnetometer and Hall sensor
A magnetometer measures the magnitude of the magnetic field in the surrounding world. It also takes measurements in three-dimensional space (along three axes of Cartesian coordinates - X, Y and Z). The main function of the magnetometer is to more accurately determine the location during navigation. In this mode of use it functions as a digital compass. Due to the fact that one of the axes, which is located in the plane with the North Pole of the Earth, registers a constantly increased background. The magnetometer helps to more accurately determine in which direction relative to north the smartphone is moving.

Smartphone magnetometer
A magnetometer is often called a Hall sensor, but these are not entirely identical concepts. We wrote more about the Hall sensor in another article. The differences are that the first is more universal and sensitive. The magnetometer is capable of measuring magnetic radiation, while only registering its presence/absence and decrease/increase. In modern smartphones, a separate Hall sensor is usually not installed, since a universal magnetometer completely covers its functionality.
One of the alternative functions of a magnetometer is to find wiring in walls. A live conductor generates weak electromagnetic radiation, and the sensitivity of the sensor is units of microtesla. If you move your smartphone along the wall, the magnetic background will be increased where the cable is laid.
Gravity sensor
Measures the force of gravity of our planet in three-dimensional space. At rest (when the smartphone is lying on the table), its readings should coincide with the accelerometer: along one of the axes the gravitational force will be close to 9.8 m/s 2 . This sensor is usually not used on its own, but it helps the work of others. In navigation mode, it determines which side of the earth's surface is in order to quickly determine the correct position of the smartphone. When used in VR, the gravity sensor ensures the correct positioning of the image.
Linear acceleration sensor in a smartphone
The principle of its operation is almost identical to the accelerometer, the only difference lies in inertia. That is, the readings of this sensor do not depend on any global external factors (like gravity). The only thing it registers is the speed of the smartphone’s movements in space relative to its previous position.
The linear acceleration sensor is not capable of determining the position of the device in space (there is no reference to external landmarks), but this is not necessary (the gravity sensor and accelerometer do an excellent job of this task). The absence of reference to external landmarks allows you to rotate objects on the display without reference to these landmarks, for example, in games. Also, this sensor, in combination with others, increases the overall accuracy of movement detection.
Rotation sensor
It determines the direction and frequency of rotation of the smartphone relative to one of the axes of three-dimensional space. Like the acceleration sensor, it is independent and not tied to external reference points. Often performed as part of a single module with a linear acceleration sensor. Separately, as a rule, it is not used, but it allows you to adjust the operation of other sensors to improve accuracy. It also helps with gesture control, for example, by twisting the smartphone in your hand, the camera is activated.

Cutaway MEMS gyroscope
Temperature sensors
A modern smartphone is abundantly stuffed with digital thermometers. Structurally, they are a thermocouple: a resistor with two terminals, the resistance between which varies depending on the temperature. Since it is relatively primitive, it can even be implemented inside a semiconductor chip.
Every smartphone must have a battery temperature sensor. If it overheats, it turns off charging or reduces the output current to prevent the electrolyte from boiling, which leads to a fire or explosion. Thermometers inside the SoC are also common (from a couple of pieces to a dozen or more). They measure the temperatures of processor cores, graphics accelerators, and various controllers. Sometimes there are also ambient temperature sensors, but they are not widespread. The reason for this is low accuracy, since heat from the inside of the device and the user’s hands distorts the readings.
Pressure sensor (barometer) in a smartphone
The barometer on your smartphone measures atmospheric pressure (in mmHg, bar or pascals). It allows you to more accurately determine your location and altitude above sea level, since the pressure decreases as you rise. It can also be used as an altimeter, measuring altitude above sea level, but the accuracy leaves much to be desired, since atmospheric pressure changes with the weather. The function of adjusting the weather forecast in meteorological programs and widgets is even less in demand.
Hygrometer
A hygrometer measures air humidity. Its main purpose is obvious, but this sensor is not popular. In theory, it can be used to correct weather forecast data. Knowing the readings, you can also control the indoor climate by turning on a humidifier or dehumidifier. The only known smartphone with a hygrometer is the old Samsung Galaxy S4.
Heart rate monitor or heart rate sensor in smartphones
The heart rate monitor is capable of measuring the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions. During sports, it makes it possible to monitor the work of the heart and adjust the load to increase the effectiveness of training. The disadvantage of a heart rate monitor is the need for close contact of the smartphone with a part of the body in which the blood vessels are close to the surface (for example, fingers) in order to catch the slightest pulsations. Because of this, it has not gained popularity in smartphones, but is found everywhere in smart watches and fitness trackers.

Heart rate monitor
You will also like:

If you remove all sensors from a smartphone, it will lose an impressive part of its functions and turn into a rather primitive device. Even actions familiar to users, such as changing the screen orientation when moving the gadget to a horizontal position and automatically turning off the display during a conversation, would not be performed without sensors.
In an effort to win competition in the market, manufacturers of modern mobile equipment equip their devices with a huge number of sensors - because this increases functionality. In this article we will talk about all known smartphone sensors, including those installed in the latest models.
Accelerometer– one of the main sensors of a smartphone; it is also called G-sensor. The function of the accelerometer is to measure the linear acceleration of the smartphone along 3 coordinate axes. Data about the movements of the device are accumulated and processed by a special controller - naturally, this happens in a matter of seconds. Places a tiny sensor approximately in the center of the smartphone body. Replacing the accelerometer yourself in the event of a breakdown is impossible - you will have to go to a service center.
Who should thank developers for accelerometers in smartphones? First of all, fans of racing simulators, who are able to control virtual cars by simply tilting the device left and right. It is the accelerometer that allows the gadget to change the screen orientation from portrait to landscape when the user turns the device over.
For the first time, an accelerometer appeared on a phone 5500 . This sensor caused great delight among supporters of an active lifestyle, because it allowed them to use a pedometer.
The accelerometer has one significant drawback: it can only fix the position when acceleration– that is, when the gadget moves in space. The accelerometer is not capable of determining the position of the device lying on the table. A “partner” sensor called . This sensor measures the speed of angular rotation and provides higher data accuracy compared to an accelerometer. A gyroscope that has undergone the calibration procedure will have an error of no more than 2 degrees.

The gyroscope is actively used in mobile games - in combination with an accelerometer. In addition, this sensor makes possible cameras, creating panoramic images (the gyroscope determines how many degrees the smartphone has been rotated), and gesture control.
The first smartphone with a gyroscope was 4 . Now the gyroscope is far from exotic; Most modern devices are equipped with it (as well as an accelerometer).
Proximity and light sensors
The presence of a proximity sensor (Proximity Sensor) in a smartphone is an objective necessity. If such a sensor were absent, the user would have to endure inconvenience every time while talking on the phone. It would be enough to easily touch the reset button with your cheek - and the conversation is stopped, you need to call the subscriber again. The function of the proximity sensor is obvious: it locks the gadget's screen as soon as the user brings the device to his ear. This sensor allows the smartphone owner not only to communicate comfortably, but also to save battery power.
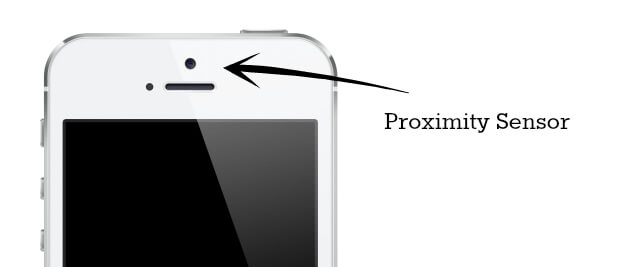
The proximity sensor is “hidden” under the front glass of the mobile device. It consists of 2 elements: diode And detector. The diode sends an infrared pulse (invisible to the human eye), and the detector tries to catch its reflection. If the detector succeeds, the screen goes dark. The sensor is capable of recording only 2 states: “ foreign object closer than 5 cm" And " foreign object more than 5 cm».
The company has achieved amazing results in experiments with a proximity sensor. Based on this sensor, the Korean manufacturer created gesture sensor, thanks to which contactless control of a smartphone became possible. The first gesture sensor appeared on the Samsung Galaxy S3 - in 2012 it was a real breakthrough.
It is not for nothing that the Light Sensor is considered in tandem with a proximity sensor - as a rule, these two sensors are located in close proximity to each other. The light sensor is the “oldest” of all sensors used in mobile electronics. It is also the simplest - from a design point of view, this sensor is a semiconductor that is sensitive to the flow of photons. The function of the light sensor is not as important as that of the proximity sensor: the Light Sensor only adjusts the brightness of the display in accordance with the surrounding conditions.

Some Samsung models (such as Galaxy Note 3 and Galaxy S5) have RGB sensors. The RGB sensor is capable of not only changing the brightness of the display, but also adjusting the proportions of red, green, blue and white colors of the image on the screen.
The developers of Samsung Galaxy Note 4 went to the point of absurdity: they taught the sensor to measure illumination in the ultraviolet range, which is invisible to humans. Thanks to this interesting innovation, the user can, for example, choose the optimal time for tanning.
Barometer and temperature sensor
A person with high sensitivity to sudden changes in atmospheric pressure simply needs to have a barometer application on their smartphone. On Google Play, for example, one of these programs is called “Barometer”.

The barometer sensor is capable of not only warning the user about the approach of a cyclone - anticyclone; This is not even its main function. The sensor increases the efficiency and accuracy of the gadget's GPS navigator. GPS satellites show where in the world the location you are looking for is located - but not at what height. This shortcoming of their work is eliminated by the barometer. A pressure sensor can help find, say, the office of a certain company in a multi-story business center building.
Temperature sensors, unlike barometers, are present in most smartphones - but you cannot measure the temperature outside with their help. This is about internal thermometers, whose task is to ensure that the gadget does not overheat. One smartphone can have a lot of similar sensors: the first controls the graphics accelerator, the second controls the processor cores, and so on. If overheating occurs, the internal thermometer automatically stops charging or reduces the output amperage.
External thermometers They are also found on gadgets, but they are still “a novelty.” The first smartphone with a built-in thermometer was the Samsung Galaxy S4. The sensor turned out to be necessary to improve the performance of the pre-installed S Health application.

Unfortunately, external thermometers of mobile devices have a significant drawback - low accuracy. The data is distorted due to the heat emanating from the user’s body and the insides of the device itself. The developers have not yet been able to solve this problem.
For the needs of the S Health application, another interesting sensor was installed on the Samsung Galaxy S4 - hygrometer. This sensor measures humidity levels, giving the user the ability to effectively control the indoor climate.
What sensors allow you to monitor your health?
A person who wants to lead a healthy lifestyle would do well to acquire a gadget that is equipped with the following sensors.
Pedometer (pedometer)
The function of the pedometer is to count the distance covered by the user based on the number of steps taken. An accelerometer can also perform this function, but the accuracy of its measurements leaves much to be desired. The pedometer as a separate sensor first appeared on the Nexus 5 smartphone.
Pulse monitor (heartbeat sensor)
The built-in heart rate monitor is one of the innovations of the Samsung Galaxy S5. Samsung developers felt that it was the pulse sensor that the S Health program lacked in order for it to be considered a full-fledged personal trainer. The Samsung heart rate monitor has not yet become popular among users, because it is quite finicky. To provide accurate data, the sensor needs close contact with a part of the user's body where blood vessels are shallow, such as the pad of a finger. Going for a run while holding your finger on the sensor is not a pleasant experience.
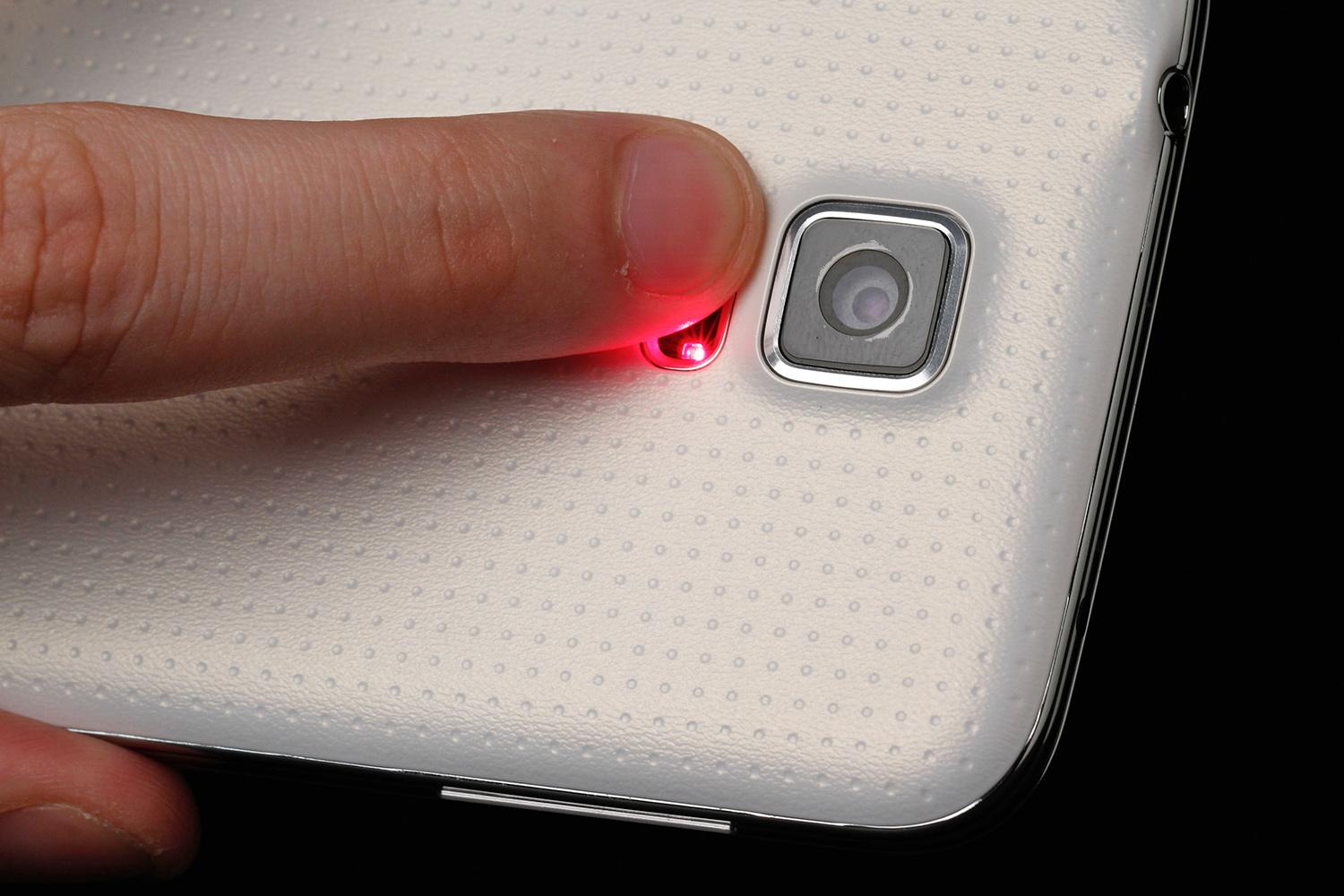

Blood oxygenation sensor (SpO2 sensor)
This sensor determines the degree of oxygen saturation in the blood. It is present only on 2 Samsung smartphones (Galaxy Note 4 and Note Edge) and is “tailored” for the S Health application. On the devices, the SpO2 sensor is combined with a camera flash and a heart rate monitor. The user just needs to activate the corresponding application and place his finger on the flash for 30-40 seconds - after which he will see the measurement result as a percentage on the gadget’s screen.
Dosimeter
The Pantone 5 smartphone released in Japan is equipped with such a sensor. The function of the dosimeter is to measure radiation. For the Japanese, this function is important, because after the accident at the Fukushima nuclear power plant in 2011, they are forced to more closely monitor the background radiation. There are no smartphones with dosimeters on the European market.
Fingerprint and retina scanners
Users who believe that the first one appeared on the iPhone 5S are greatly mistaken. Phones capable of scanning fingerprints have been released before. Back in 2004, Pantech GI 100, equipped with similar technology, was sold. 7 years later, it introduced the Atrix 4g model with a fingerprint sensor. In both cases, users reacted rather coolly to the technology.
When, in 2013, Apple built the iPhone 5S into the Home button, the Apple company was applauded by both experts and ordinary consumers. Apple was more fortunate with the era: in the “zero” the issue of the security of non-cash payments was not so pressing.
The fingerprint scanner eliminates the need for the user to use digital passwords to protect data stored on the gadget. Passwords are easy to crack; It is much more difficult to deceive a fingerprint sensor (although it is also possible).
Nowadays it has become fashionable to install fingerprint scanners in smartphones. This technology is used not only by long-term market leaders - Samsung, Apple,. However, this technology became discussed only after Samsung turned to it - they installed it in the Galaxy Note 7 iris scanner.
The sensor in the Note is different from those found in smartphones from Chinese companies. Samsung's idea can be called revolutionary because the Note 7 has a camera that is responsible only for eye scanning. The “Chinese” read information from the retina with a selfie camera.
The method used by gadgets from the Middle Kingdom is ineffective. The fact is that the eye needs to be scanned with an infrared (IR) beam, but on front cameras the IR spectrum is usually filtered - because it deteriorates. It turns out that Samsung is so far the only smartphone manufacturer that does not force users to make a choice between high-quality devices and the security of personal data.
Conclusion
Every modern smartphone is equipped with at least 5 sensors. In flagship models, the number of sensors reaches the “damn dozen”, and manufacturers are not going to stop there. IBM experts predict that already in 2017, gadgets will have a sense of smell, thanks to which they will be able to warn the user, for example, about a high concentration of fumes and the presence of influenza virus in the air. We are looking forward to innovations - surely there will be a continuation?
