Is it possible to install linux on a tablet. Instructions: Installing the Linux operating system on an Android smartphone (tablet)
Today, two operating systems occupy the leading niches in the mobile segment - these are iOS and Android. Many manufacturers are closely engaged in the creation of their own mobile systems. Some attempts have been successful. Their result was, at best, a few devices that never gained success in the market. Ubuntu Touch was announced in 2013.
Put on phones mobile version Linux systems - Ubuntu Touch.
It had some interest from users. Ubuntu Touch, which can be installed on a smartphone today, offers the user not only new interface. It will be of interest to enthusiasts, as well as to all fans of the Linux OS. And just for those who are tired of the monotony of mobile platforms.
Mobile platform Ubuntu Touch appeared 4 years ago. She gained quite wide popularity - this was facilitated by the well-known desktop "mother" of the new mobile system. But Ubuntu did not become a popular version on the phone. The reason for this was the low stability, a large number of bugs. Devices running this OS often rebooted, and the shell was not the height of design thought.
In the press, many times returned to the topic of this operating system. Rumors were very different - both about the freezing of the platform, and about the complete cessation of work on it. You can’t trust all of them, but as a fact, Ubuntu Touch appears quite rarely on smartphones. AT recent times there is information about significant platform updates and this gives hope to all fans of the mobile OS that Canonical has not forgotten about a promising product.

As part of the project mobile version Ubuntu has two separate global versions- for smartphones and tablets. They are called respectively - Phone and Tablet. They practically do not differ for the end user, and the differences are aimed rather at supporting the hardware platform.
Key Features
The desktop version of the OS uses the Unity graphical interface, which is loved by non-professionals. Linux users. In mobile, the manufacturer slightly moved away from it - only the side and top panels remained unchanged.
All basic actions in the new OS are performed by gestures. For example, if you swipe between the edges of the screen, the multitasking menu will appear on it. For users of the Android system, such a solution will be somewhat inconvenient, but innovative and unusual.
In addition, Ubuntu has a Terminal on a smartphone! This is still an inferior version of it, and it is still far from the functionality of the desktop. However, some functions are still there, and the tricks work.

How to install Ubuntu on Android?
To install Ubuntu on a phone instead of Android, you need to have basic skills in working with the Android system. The installation will not remove your "native" system, it will be done on top of an existing distribution.
IMPORTANT. You perform all actions at your own peril and risk.
- Android App Required - Linux Deploy. You can find it in the Play Market.
- Launch the program and study the help menu on the screen. You should see a suggested course of action.
- If necessary, go to "Settings" and select the Russian interface language.
- Create new profile for accounting linux entries. To do this, in the main screen of the program, click on the line "Linux". It is located at the top.
- Click the OK button. It remains only to select the desired profile.
- And now you need File manager. Your best bet is to use ES Explorer. Open it. AT root directory create Ubuntu folder. It is very important to write the name on English language. OS files will be installed to this folder.
- Record the path to the folder in a separate location. He'll still be useful.
- Restart the Linux Deploy program. In the options, select "Distribution" - "Ubuntu". After that, you should start downloading Ubuntu on your smartphone.
- When the installation is completed, click on the "Start" button. You will see service messages. They say that the process of deploying the OS is underway.
- Download and install the VNCViewer application. You will need it to get more information. Password account default is changeme.
- That's all! Now your smartphone or tablet is fully installed workable copy Ubuntu!
Installing Ubuntu Phone
We looked at installing a full-fledged Ubuntu on mobile device. Installing Ubuntu Mobile on a smartphone - more simple task. It can be run from the desktop version of this operating system.
Detailed instructions for the transformation of any device running under Android control, in full computer based on Linux.
Running Linux on Android is possible! And you don’t need a device with root rights for this: all the necessary software is available in official store Google Play. In just 10–15 minutes, you can get an operating system that differs from Android in advanced functionality.
Note: if you follow our instruction, Linux OS will be launched in virtual environment. Android will still work in background. It would be wrong to call such a system complete. However, with a list standard tasks she's doing well.
Please close everything before installation. not desired applications and clear the RAM of your Android device.
1. From google store Play install GNURoot Debian and XServer XSDL .
2. Before the beginning Linux installations make sure your device is connected to a stable WiFi networks. Start GNURoot. Download will start required packages environment.
Installation takes from 30 seconds to several minutes depending on the speed of your Internet connection. Ignore the running lines until the following inscription appears:
Let this line not scare those familiar with the concept of "root-rights": the application will not cause any harm to the device, since it works in a "sandbox".
3. Enter the following command:
apt-get update
Wait for the packages to finish downloading. This will be indicated by the line Reading package lists…Done.
4. Now enter another line:
apt-get upgrade
To the question "Do you want to continue?" enter English letter Y and press Enter. The package installation will begin.
This time, the installation procedure will take a little longer. Patiently wait for the installation to complete until the cherished line appears:
The Debian Linux environment is installed, and now you can proceed to deployment graphic shell.
5. Installing all packages of a Linux distribution is done with the following command:
apt-get install lxde
There is also an option to install the system kernel using the line:
apt-get install lxde-core
Confirm the setting by re-entering Y and clicking on Enter key. The package download process will begin.
During installation, make sure that all the files have been successfully downloaded, and that your device has not run out when unpacking free space. Otherwise, the system startup will fail.
6. Three additional utilities must be downloaded to complete the installation of the operating system:
- XTerm - for accessing the terminal from the Linux graphical shell;
- Synaptic Package Manager - for managing apt packages and application downloads;
- Pulseaudio - for installing sound drivers.
All three utilities are installed with a single GNURoot terminal command:
apt-get install xterm synaptic pulseaudio
Approximately 260 MB of data will be downloaded to the device.
7. Now minimize the GNURoot application and open the previously installed XServer XSDL. Agree to download additional fonts. After the installation is complete, tap the screen several times (the application will prompt you to select the resolution and font size - it all depends on your preferences) until you see a splash screen with a blue background and white text.
Restart GNURoot and enter the following two commands in turn:
export DISPLAY=:0 PULSE_SERVER=tcp:127.0.0.1:4712
startlxde &
The sequence of further restart of the system (when you want to open Linux again) looks like this: start XServer XSDL and wait for the appearance blue screen, open GNURoot and enter the above two commands, you return to XServer XSDL.
If the terminal swears at an invalid command, go back to step 5 of this manual and try installing a bare kernel. Check the memory status of your Android device.
8. Now open XServer XSDL, wait a few seconds - and you have Linux ready to go.
To install applications in the lower left corner, open the Start menu and select Run. Type Synaptic and press Enter.
In the window that opens, use the search and install the necessary applications. It could be Firefox browser, editor GIMP images, the Libre office suite, and other Linux-compatible programs.
Of course, this Linux installation option cannot be called full launch operating system on Android. Virtual Linux has several limitations, but when using wireless mice and keyboard (it is also possible to connect using an OTG adapter and a USB hub), you can turn your smartphone or tablet into laptop with the functionality of an adult OS.
Most Android users know that this platform is based on the operating system Linux systems, but despite this, many of its programs are not available. That is why a great way out is to put a Linux shell called Ubuntu on the tablet. It runs through the Emulator and runs in parallel with Android, providing a wide range of applications that are not usually loaded on devices with this operating system.
Both operating systems can run in parallel
We will look at how to install it yourself without help. special applications, using only the emulator and VNC Viewer.
Installing Ubuntu on a Tablet
What parameters are required for this shell? We need root rights free memory in the amount of 2.5–3.5 GB. Requires a minimum clock frequency in size from 1 GHz, support for the Ext2 file system is required. As a means of facilitating the installation, we need several programs, including an emulator - it will be useful for further running the software.
What are root rights, and how to get them? They represent administrator rights. In this case, the presence of such rights will allow changing system parameters tablet, so install Ubuntu without them for Android will not work.

You can get these rights through various applications, a large number of which you will find in Play market. Download one of them, activate administrator rights and then proceed to the direct installing Ubuntu on a tablet.
To do this, do the following:
- Sign in to system settings on your tablet and in the "For Developers" section, enable USB debugging mode. If you do not have this function, go to the "About device" menu and find the line with the build number - quickly click on it 5 times in a row, after which a message will appear that you have become a developer and should appear in the list;

- Create a folder called Ubuntu in the card's memory;
- Download the script for Linux startup and one of the software assemblies - there are only two of them. The first is minimal, contains only individual, most popular applications and has a size of half a gigabyte, after installation it takes up 2.5 GB on the memory card free space. The second is a complete assembly, has an extensive set of programs, respectively, has original size 1.5 GB and after unpacking will take 3.5 GB of memory;
- Next, you should download two programs: terminal emulator for Android and VNC Viewer;
- Open the Emulator application and run the following commands in it:
- cd /sdcard/ubuntu
- sh ubuntu.sh.
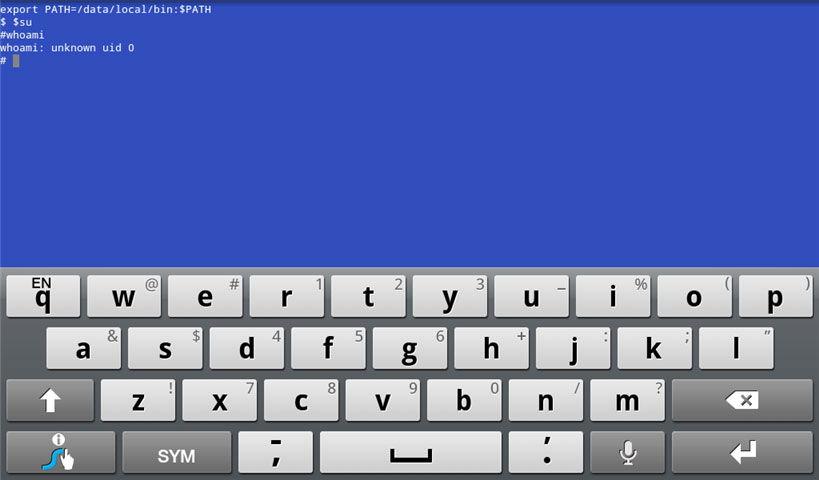
Note. Before entering commands, the emulator will require the first time you start it, and, of course, you need to give consent to this action.
- Next, you need to specify your screen resolution details and desktop environment type in the same Emulator app.
- After a few minutes at correct installation you will see a message with the text [email protected]:/# - it means that Linux shell in the emulator was successfully launched.
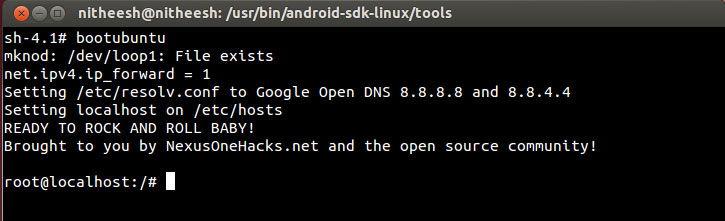


Linux Deploy. This app is open source code, designed to automate the process of installing, configuring and running GNU / Linux distributions on Android platform inside the chroot container. The application creates a disk image on a memory card or other media, mounts it and installs the selected Linux distribution there. It supports installation to a file, directly to a partition of a memory card, to a directory with the ext2 / ext3 / ext4 file system and to RAM. Applications from a Linux distribution run in a chroot environment, run in parallel with the main system and are comparable in speed to it. All changes made to the device are reversible, i.e. the application and the components created by it can be completely removed.
The Linux distribution is installed over the network from official mirrors on the Internet. Because the linux work Deploy is based on system call Linux kernels, then only Linux distributions. Through the program interface, you can manage the installation process of the Linux distribution, and after installation, you can start and stop services installed system(there is support for running your own scripts). The installation progress is displayed as text reports in the application's main window. During installation, the program itself sets up the working environment, which includes the base system, SSH server, VNC server, and a graphical environment of your choice. Also, through the program interface, you can control the parameters SSH servers and VNC.
Installing a Linux distribution takes about 30 minutes. Recommended minimum size disk image without GUI - 512 MB, and with GUI- 1024 MB (for LXDE). After initial installation the password for SSH and VNC access is assigned as "changeme", which can be changed standard means distribution, or through the application settings.
Characteristics:
- Supported distributions: Debian, Ubuntu, Kali Linux, Arch Linux, Fedora, CentOS, Gentoo, openSUSE, Slackware, RootFS (tgz, tbz2, txz)
- Installation type: file, partition, RAM, directory
- Supported file systems: ext2, ext3, ext4
- Supported architectures: ARM, ARM64, x86, x86_64, architecture emulation mode (ARM<->x86)
- Container connection methods: CLI, SSH, VNC, X server, framebuffer
- Management interfaces (CLI): Android terminal (or adb), telnet, web interface (terminal via browser)
- Desktop environment: XTerm, LXDE, Xfce, MATE, other (manual setting)
- Supported languages: multilingual interface
ATTENTION!
This program is supplied WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY, and the author is not responsible for any possible consequences its use. It's free software, and you may distribute it under the terms of the GPLv3 license.
GNU/LINUX INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
- Connect to WiFi or other network with internet access. The installation is done over the network and will not work without Internet access.
- Make sure your device has received superuser rights (root). Install latest version Linux programs Deploy and run it.
- When the application is launched for the first time, the working environment is automatically updated, which is a directory containing all the necessary scripts, settings, and container profiles. Work environment settings can be viewed in the " Settings -> Working environment". The environment directory should not be changed unless there is a reason to. It is useful to leave the " Settings -> Do not turn off the screen" ("Settings -> Screen Lock") while the app is active, the screen, WiFi and processor will not go to sleep.
- The program supports working with several profiles, where the parameters of each instance of GNU/Linux are stored. You can quickly switch between instances through the profile management window (opened by clicking on the icon in the title of the main window). By default, a profile named "linux" is created. Go to the parameters of the current profile (extreme right button) and configure the necessary installation and startup options for the GNU/Linux distribution ( see parameter description).
- Linux Deploy 2.x does not require mandatory installation to the BusyBox system, but in rare cases it may be necessary to use the system BusyBox. To do this, set compatible ®BusyBox. In the BusyBox options before installation, you must select the option " Replace applets". After that, in the settings of the desktop Linux environments Deploy, you need to specify the path to the system BusyBox in the " Settings -> PATH Variable" ("Settings -> PATH variable"), for example, /system/xbin, and start updating the working environment " Settings -> Update environment" ("Settings -> Update ENV").
- Run the installation of the selected distribution: " Menu -> Install" ("Menu -> Install"). The installation log is displayed in the main window of the application. The installation takes approximately 30 minutes on average. The image creation step may take more than 2 GB long time(about 15 min.).
- If the installation completed without errors, then you can start the Linux system with the " START" ("START"). This will start the services marked in the parameters - SSH, VNC and others.
- To access the console of a Linux system via SSH, you must install ConnectBot (or another SSH client). To access the desktop of a Linux system, you must install an X server, such as XServer XSDL . In the settings you should specify the IP of the device to connect, for the same device - 127.0.0.1. The password for SSH and VNC is specified in the container parameters. Change password current user It is possible from the console with the passwd command. To run programs as root, use the sudo command (for example, sudo synaptic). By default, the root user (unless it is specified in the settings as a username) has no password, but you can set a password for it sudo command passwd root.
- To stop the Linux system, all services running under it and unmount the disks, just click the " STOP" ("STOP").
- Linux Deploy allows you to manage containers through CLI (interface command line). To access the CLI, you can use telnet or a web browser, after activating the appropriate management interfaces in the settings.
- To reduce installation time basic system or in case of problems with installing the system from the official repositories, you can import the container from a pre-prepared archive. To do this, there is a repository of containers created using Linux Deploy and available through the application interface in the " repository" ("repository"). Just select the desired container in the repository interface and click the " Import" ("Import"). After that, a new profile will be created in the application, the parameters of which can be changed if necessary. Then you just need to run the installation " Menu -> Install" ("Menu -> Install"), this will prepare the installation path (create an image for the container), download the container archive, unpack and configure. After the procedure is completed, you can start the container with the button " START" ("START").
PROGRAM UPDATE
After updating the program, the working environment is automatically updated. If necessary, the update can be started manually: " Settings -> Update environment" ("Settings -> Update ENV"). Program (environment) updates do not affect an already installed GNU/Linux system, i.e. an installed system cannot be damaged or changed in any way due to an update.
To change the settings of an already installed system or to return the settings to the original, you need to configure: " Menu -> Configure" ("Menu -> Configure"). If some components are selected in the parameters, then the configuration will install packages for the selected components.
UNINSTALL A PROGRAM
Before uninstalling the program, you need to stop the GNU / Linux distribution with the button STOP, if it is not possible to stop the distribution kit, then it is recommended to reboot the device. After that run the command " Settings -> Delete environment" ("Settings -> Remove ENV"). After that, you can delete the application. Deleting an application with an unmounted container is dangerous, when deleting an application of a version below 1.5.3, all data from all partitions mounted in the container are also deleted! There may also be .img files that are created on the memory card when installing distributions , such files can be deleted manually through any file manager.
Download application for installing Linux on Android - Linux Deploy on Android you can follow the link below.


Linux Deploy. This is an open source application designed to automate the process of installing, configuring and running GNU/Linux distributions on the Android platform inside a chroot container. The application creates a disk image on a memory card or other media, mounts it and installs the selected Linux distribution there. It supports installation to a file, directly to a partition of a memory card, to a directory with the ext2 / ext3 / ext4 file system and to RAM. Applications from a Linux distribution run in a chroot environment, run in parallel with the main system and are comparable in speed to it. All changes made to the device are reversible, i.e. the application and the components created by it can be completely removed.
The Linux distribution is installed over the network from official mirrors on the Internet. Since Linux Deploy is based on the Linux kernel system call, only Linux distributions can act as "guest" systems. Through the program interface, you can manage the installation process of the Linux distribution, and after installation, you can start and stop the services of the installed system (there is support for running your own scripts). The installation progress is displayed as text reports in the application's main window. During installation, the program itself sets up the working environment, which includes the base system, SSH server, VNC server, and a graphical environment of your choice. Also, through the program interface, you can manage the parameters of SSH and VNC servers.
Installing a Linux distribution takes about 30 minutes. Recommended minimum disk image size without GUI is 512 MB, and with GUI is 1024 MB (for LXDE). After the initial installation, the password for access via SSH and VNC is assigned as "changeme", which can be changed using the standard distribution tools, or through the application settings.
Characteristics:
- Supported distributions: Debian, Ubuntu, Kali Linux, Arch Linux, Fedora, CentOS, Gentoo, openSUSE, Slackware, RootFS (tgz, tbz2, txz)
- Installation type: file, partition, RAM, directory
- Supported file systems: ext2, ext3, ext4
- Supported architectures: ARM, ARM64, x86, x86_64, architecture emulation mode (ARM<->x86)
- Container connection methods: CLI, SSH, VNC, X server, framebuffer
- Management interfaces (CLI): Android terminal (or adb), telnet, web interface (terminal via browser)
- Desktop environment: XTerm, LXDE, Xfce, MATE, other (manual setting)
- Supported languages: multilingual interface
ATTENTION!
This program is supplied WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY, and the author is not responsible for any possible consequences of its use. This is free software and you may distribute it under the terms of the GPLv3 license.
GNU/LINUX INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
- Connect to WiFi or other network with internet access. The installation is done over the network and will not work without Internet access.
- Make sure your device has received superuser rights (root). Install the latest Linux Deploy program and run it.
- When the application is launched for the first time, the working environment is automatically updated, which is a directory containing all the necessary scripts, settings, and container profiles. Work environment settings can be viewed in the " Settings -> Working environment". The environment directory should not be changed unless there is a reason to. It is useful to leave the " Settings -> Do not turn off the screen" ("Settings -> Screen Lock") while the app is active, the screen, WiFi and processor will not go to sleep.
- The program supports working with several profiles, where the parameters of each instance of GNU/Linux are stored. You can quickly switch between instances through the profile management window (opened by clicking on the icon in the title of the main window). By default, a profile named "linux" is created. Go to the settings of the current profile (far right button) and configure the necessary options for installing and running the GNU/Linux distribution ( see parameter description).
- Linux Deploy 2.x does not require mandatory installation on the BusyBox system, however, in rare cases, it may be necessary to use the system BusyBox. To do this, set compatible ®BusyBox. In the BusyBox options before installation, you must select the option " Replace applets". After that, in the settings of the Linux Deploy working environment, you need to specify the path to the system BusyBox in the " Settings -> PATH Variable" ("Settings -> PATH variable"), for example, /system/xbin, and start updating the working environment " Settings -> Update environment" ("Settings -> Update ENV").
- Run the installation of the selected distribution: " Menu -> Install" ("Menu -> Install"). The installation log is displayed in the application's main window. The installation takes about 30 minutes on average. The image creation step can take a long time (about 15 minutes) if the size is larger than 2 GB.
- If the installation completed without errors, then you can start the Linux system with the " START" ("START"). This will start the services marked in the parameters - SSH, VNC and others.
- To access the console of a Linux system via SSH, you must install ConnectBot (or another SSH client). To access the desktop of a Linux system, you must install an X server, such as XServer XSDL . In the settings you should specify the IP of the device to connect, for the same device - 127.0.0.1. The password for SSH and VNC is specified in the container parameters. You can change the password of the current user from the console with the passwd command. To run programs as root, use the sudo command (for example, sudo synaptic). By default, the root user (unless it is configured as a username) has no password set, but you can set a password for it with the sudo passwd root command.
- To stop the Linux system, all services running under it and unmount the disks, just click the " STOP" ("STOP").
- Linux Deploy allows you to manage containers through the CLI (Command Line Interface). To access the CLI, you can use telnet or a web browser, after activating the appropriate management interfaces in the settings.
- To reduce the time to install the base system, or in case of problems installing the system from the official repositories, you can import the container from a pre-prepared archive. To do this, there is a repository of containers created using Linux Deploy and available through the application interface in the " repository" ("repository"). Just select the desired container in the repository interface and click the " Import" ("Import"). After that, a new profile will be created in the application, the parameters of which can be changed if necessary. Then you just need to run the installation " Menu -> Install" ("Menu -> Install"), this will prepare the installation path (create an image for the container), download the container archive, unpack and configure. After the procedure is completed, you can start the container with the button " START" ("START").
PROGRAM UPDATE
After updating the program, the working environment is automatically updated. If necessary, the update can be started manually: " Settings -> Update environment" ("Settings -> Update ENV"). Program (environment) updates do not affect an already installed GNU/Linux system, i.e. an installed system cannot be damaged or changed in any way due to an update.
To change the settings of an already installed system or to return the settings to the original, you need to configure: " Menu -> Configure" ("Menu -> Configure"). If some components are selected in the parameters, then the configuration will install packages for the selected components.
UNINSTALL A PROGRAM
Before uninstalling the program, you need to stop the GNU / Linux distribution with the button STOP, if it is not possible to stop the distribution kit, then it is recommended to reboot the device. After that run the command " Settings -> Delete environment" ("Settings -> Remove ENV"). After that, you can delete the application. Deleting an application with an unmounted container is dangerous, when deleting an application of a version below 1.5.3, all data from all partitions mounted in the container are also deleted! There may also be .img files that are created on the memory card when installing distributions , such files can be deleted manually through any file manager.
Download application for installing Linux on Android - Linux Deploy on Android you can follow the link below.
