Detailed review and testing of the Apple iPad mini with Retina display. A mobile network is a radio system that allows multiple mobile devices to communicate with each other
Information about the make, model, and alternative names of the specific device, if available.
Design
Information about the dimensions and weight of the device, presented in different units of measurement. Materials used, colors offered, certificates.
| Width Width information - refers to the horizontal side of the device in its standard orientation during use. | 200 mm (millimeters) 20 cm (centimeters) 0.66 ft (feet) 7.87 in (inches) |
| Height Height information - refers to the vertical side of the device in its standard orientation during use. | 134.7 mm (millimeters) 13.47 cm (centimeters) 0.44 ft (feet) 5.3 in (inches) |
| Thickness Information about the thickness of the device in different units of measurement. | 7.2 mm (millimeters) 0.72 cm (centimeters) 0.02 ft (feet) 0.28 in (inches) |
| Weight Information about the weight of the device in different units of measurement. | 308 g (grams) 0.68 lbs 10.86 oz (ounces) |
| Volume The approximate volume of the device, calculated based on the dimensions provided by the manufacturer. Refers to devices with the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped. | 193.97 cm³ (cubic centimeters) 11.78 in³ (cubic inches) |
| Colors Information about the colors in which this device is offered for sale. | Silver |
Operating system
An operating system is a system software that manages and coordinates the operation of hardware components in a device.
SoC (System on Chip)
A system on a chip (SoC) includes all the most important hardware components of a mobile device on one chip.
| SoC (System on Chip) A system on a chip (SoC) integrates various hardware components, such as a processor, graphics processor, memory, peripherals, interfaces, etc., as well as the software necessary for their operation. | Apple A5 APL2498 |
| Technological process Information about the technological process by which the chip is manufactured. Nanometers measure half the distance between elements in the processor. | 32 nm (nanometers) |
| Processor (CPU) The primary function of a mobile device's processor (CPU) is to interpret and execute instructions contained in software applications. | ARM Cortex-A9 |
| Processor size The size (in bits) of a processor is determined by the size (in bits) of the registers, address buses, and data buses. 64-bit processors have higher performance compared to 32-bit processors, which in turn are more powerful than 16-bit processors. | 32 bit |
| Instruction Set Architecture Instructions are commands with which the software sets/controls the operation of the processor. Information about the instruction set (ISA) that the processor can execute. | ARMv7 |
| Level 1 cache (L1) Cache memory is used by the processor to reduce access time to more frequently used data and instructions. L1 (level 1) cache is small in size and works much faster than both system memory and other cache levels. If the processor does not find the requested data in L1, it continues to look for it in the L2 cache. On some processors, this search is performed simultaneously in L1 and L2. | 32 kB + 32 kB (kilobytes) |
| Level 2 cache (L2) L2 (level 2) cache is slower than L1 cache, but in return it has a higher capacity, allowing it to cache more data. It, like L1, is much faster than system memory (RAM). If the processor does not find the requested data in L2, it continues to look for it in the L3 cache (if available) or in RAM memory. | 1024 kB (kilobytes) 1 MB (megabytes) |
| Number of processor cores The processor core executes software instructions. There are processors with one, two or more cores. Having more cores increases performance by allowing multiple instructions to be executed in parallel. | 2 |
| CPU clock speed The clock speed of a processor describes its speed in terms of cycles per second. It is measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). | 1000 MHz (megahertz) |
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) handles calculations for various 2D/3D graphics applications. In mobile devices, it is most often used by games, consumer interfaces, video applications, etc. | PowerVR SGX543 MP2 |
| Number of GPU cores Like a CPU, a GPU is made up of several working parts called cores. They handle graphics calculations for various applications. | 2 |
| Amount of random access memory (RAM) Random access memory (RAM) is used by the operating system and all installed applications. Data stored in RAM is lost after the device is turned off or restarted. | 512 MB (megabytes) |
| Type of random access memory (RAM) Information about the type of random access memory (RAM) used by the device. | LPDDR2 |
Built-in memory
Each mobile device has built-in (non-removable) memory with a fixed capacity.
Screen
The screen of a mobile device is characterized by its technology, resolution, pixel density, diagonal length, color depth, etc.
| Type/technology One of the main characteristics of the screen is the technology by which it is made and on which the quality of the information image directly depends. | IPS |
| Diagonal For mobile devices, screen size is expressed by the length of its diagonal, measured in inches. | 7.9 in (inches) 200.66 mm (millimeters) 20.07 cm (centimeters) |
| Width Approximate screen width | 6.32 in (inches) 160.53 mm (millimeters) 16.05 cm (centimeters) |
| Height Approximate screen height | 4.74 in (inches) 120.4 mm (millimeters) 12.04 cm (centimeters) |
| Aspect Ratio The ratio of the dimensions of the long side of the screen to its short side | 1.333:1 4:3 |
| Permission Screen resolution shows the number of pixels vertically and horizontally on the screen. Higher resolution means clearer image detail. | 1024 x 768 pixels |
| Pixel Density Information about the number of pixels per centimeter or inch of the screen. Higher density allows information to be displayed on the screen with clearer detail. | 162 ppi (pixels per inch) 63 ppcm (pixels per centimeter) |
| Color depth Screen color depth reflects the total number of bits used for color components in one pixel. Information about the maximum number of colors that the screen can display. | 24 bit 16777216 flowers |
| Screen area Approximate percentage of screen area occupied by the screen on the front of the device. | 71.97% (percent) |
| Other characteristics Information about other screen features and characteristics. | Capacitive Multi-touch |
| LED-backlit Oleophobic (lipophobic) coating |
Sensors
Different sensors perform different quantitative measurements and convert physical indicators into signals that a mobile device can recognize.
Rear camera
The main camera of a mobile device is usually located on its back panel and may be combined with one or more secondary cameras.
| Image Resolution One of the main characteristics of cameras is resolution. It represents the number of horizontal and vertical pixels in an image. For convenience, smartphone manufacturers often list resolution in megapixels, indicating the approximate number of pixels in millions. | 2592 x 1944 pixels 5.04 MP (megapixels) |
| Video resolution Information about the maximum video resolution that the camera can record. | 1920 x 1080 pixels 2.07 MP (megapixels) |
| Video recording speed (frame rate) Information about the maximum recording speed (frames per second, fps) supported by the camera at maximum resolution. Some of the most basic video recording speeds are 24 fps, 25 fps, 30 fps, 60 fps. | 30fps (frames per second) |
| Characteristics Information about additional software and hardware features of the rear (rear) camera. | Geographical tags Touch Focus Face recognition |
Front-camera
Smartphones have one or more front cameras of various designs - a pop-up camera, a rotating camera, a cutout or hole in the display, an under-display camera.
Audio
Information about the type of speakers and audio technologies supported by the device.
Radio
The radio of the mobile device is a built-in FM receiver.
WiFi
Wi-Fi is a technology that provides wireless communication for transmitting data over close distances between various devices.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a standard for secure wireless data transfer between various devices of different types over short distances.
USB
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an industry standard that allows different electronic devices to exchange data.
Headphone jack
This is an audio connector, also called an audio jack. The most widely used standard in mobile devices is the 3.5mm headphone jack.
Connecting devices
Information about other important connection technologies supported by your device.
Browser
A web browser is a software application for accessing and viewing information on the Internet.
Video file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support different video file formats and codecs, which respectively store and encode/decode digital video data.
Battery
Mobile device batteries differ from each other in their capacity and technology. They provide the electrical charge necessary for their functioning.
Specific Absorption Rate (SAR)
The SAR level refers to the amount of electromagnetic radiation absorbed by the human body while using a mobile device.
| Body SAR level (EU) The SAR level indicates the maximum amount of electromagnetic radiation to which the human body is exposed when holding a mobile device at hip level. The maximum permissible SAR value for mobile devices in Europe is 2 W/kg per 10 grams of human tissue. This standard has been established by the CENELEC Committee in compliance with the ICNIRP 1998 guidelines and IEC standards. | 0.29 W/kg (Watt per kilogram) |
| Body SAR level (US) The SAR level indicates the maximum amount of electromagnetic radiation to which the human body is exposed when holding a mobile device at hip level. The highest permissible SAR value in the USA is 1.6 W/kg per 1 gram of human tissue. This value is set by the FCC, and the CTIA monitors mobile devices' compliance with this standard. | 1.19 W/kg (Watt per kilogram) |
Advantages of the tablet:
Really “mini”, i.e. thin, light, comfortable in the hand;
- high-quality screen, rich colors, clarity, the image is visible from any angle, simply an excellent screen. The fact that the resolution is not the highest, i.e. not retina, most users will not notice it and do not need it. You can see the pixels if you try, but only if you try really hard.
- high-quality loud sound, stereo, which is even better than in ipad4.
- iOS, this is my first acquaintance with this operating system, I compare it with other “axes”. Of course, the response to finger touches is better, faster by a fraction of a second, but that’s what matters. On an iPad, a web page or a photo seems to stick to your hands when you change the scale with your fingers; the tactile sensation is still better, it’s more pleasant to work with. iPad doesn't need to be rebooted regularly or often. It’s especially touching how smoothly and smoothly the iPad flips the picture on the screen when turning the screen from landscape to portrait view and vice versa - other manufacturers do not have such beauty.
- holds a charge for a long time, i.e. At night you plug it into a socket and for the whole day you can forget about looking at “how many percent of the battery do I have left?”
- it’s pleasant to hold in your hands, the feeling of a solid, strong, expensive thing, metal body.
- no need to buy or install an antivirus program. Still, some kind of savings.
Disadvantages of the tablet:
Factory defect: the volume switch buttons “stick”. The first day they worked as they should, but from the second day you can change the volume, but you only need to press your finger on a certain part of the button and only strictly at a certain angle - if I give it to someone, then I explain, show, teach for a long time. At the same time, I did not drop or hit the tablet. Very annoying.
- If you read pdf files, then small letters are poorly drawn, as if blurred or blurred. However, this is simply perhaps the other side of the small screen coin.
- a very easily soiled metal case (black) - the back quickly gets dirty with your fingers and becomes dirty. It's difficult to scrub off.
- gave the native browser of this tablet (safari) a race to open Wikipedia Internet pages. So, if the page is large and long with a lot of pictures and text, then the mini-iPad browser will have “white spots” on the page, i.e. nothing at all - no text, no pictures - then you move the page up and down a little and the image reluctantly, belatedly, but still appears. And I checked - everything is fine with the page, apparently the mini-iPad does not have enough power or there is some kind of glitch.
- the registration procedure in Apple's "happiness store" appstore took a surprisingly long time. Some points are not explained - you have to guess at random the third time. Although I consider myself to be in the category of “advanced” users.
- The specialists from Cupertino themselves, caring Apple people, could make good instructions for iTunes. No, I downloaded their instructions on the Apple website, but they are surprisingly very brief and incomprehensible. Thanks to the step-by-step instructions from YouTube, kind people helped.
- Auto-adjustment of screen brightness does not work. Those. Although you check the box, the brightness does not change depending on the external lighting, only when you change it manually - this is the brightness that will remain. It’s strange, like a marriage or something.
Information about the make, model, and alternative names of the specific device, if available.
Design
Information about the dimensions and weight of the device, presented in different units of measurement. Materials used, colors offered, certificates.
| Width Width information - refers to the horizontal side of the device in its standard orientation during use. | 200 mm (millimeters) 20 cm (centimeters) 0.66 ft (feet) 7.87 in (inches) |
| Height Height information - refers to the vertical side of the device in its standard orientation during use. | 134.7 mm (millimeters) 13.47 cm (centimeters) 0.44 ft (feet) 5.3 in (inches) |
| Thickness Information about the thickness of the device in different units of measurement. | 7.2 mm (millimeters) 0.72 cm (centimeters) 0.02 ft (feet) 0.28 in (inches) |
| Weight Information about the weight of the device in different units of measurement. | 312 g (grams) 0.69 lbs 11.01 oz (ounces) |
| Volume The approximate volume of the device, calculated based on the dimensions provided by the manufacturer. Refers to devices with the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped. | 193.97 cm³ (cubic centimeters) 11.78 in³ (cubic inches) |
SIM card
The SIM card is used in mobile devices to store data that certifies the authenticity of mobile service subscribers.
Mobile networks
A mobile network is a radio system that allows multiple mobile devices to communicate with each other.
| GSM GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is designed to replace the analogue mobile network (1G). For this reason, GSM is often called a 2G mobile network. It is improved by the addition of GPRS (General Packet Radio Services), and later EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) technologies. | GSM 850 MHz GSM 900 MHz GSM 1800 MHz GSM 1900 MHz |
| CDMA CDMA (Code-Division Multiple Access) is a channel access method used in communications in mobile networks. Compared to other 2G and 2.5G standards like GSM and TDMA, it provides higher data transfer speeds and the ability to connect more consumers at the same time. | CDMA 800 MHz (A1455) CDMA 1900 MHz (A1455) |
| CDMA2000 CDMA2000 is a group of 3G mobile network standards based on CDMA. Their advantages include a more powerful signal, fewer interruptions and network breaks, support for an analog signal, wide spectral coverage, etc. | 1xEV-DO Rev. A (A1455) |
| UMTS UMTS is an abbreviation for Universal Mobile Telecommunications System. It is based on the GSM standard and belongs to 3G mobile networks. Developed by 3GPP and its biggest advantage is providing greater speed and spectral efficiency thanks to W-CDMA technology. | UMTS 850 MHz UMTS 900 MHz UMTS 1900 MHz UMTS 2100 MHz |
| LTE LTE (Long Term Evolution) is defined as a fourth generation (4G) technology. It is developed by 3GPP based on GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA to increase the capacity and speed of wireless mobile networks. The subsequent technology development is called LTE Advanced. | LTE 700 MHz Class 17 (A1454) LTE 850 MHz (A1455) LTE 1700/2100 MHz (A1454) LTE 1800 MHz (A1455) LTE 1900 MHz (A1455) LTE 2100 MHz (A1455) |
Mobile communication technologies and data transfer speeds
Communication between devices on mobile networks is carried out using technologies that provide different data transfer rates.
Operating system
An operating system is a system software that manages and coordinates the operation of hardware components in a device.
SoC (System on Chip)
A system on a chip (SoC) includes all the most important hardware components of a mobile device on one chip.
| SoC (System on Chip) A system on a chip (SoC) integrates various hardware components, such as a processor, graphics processor, memory, peripherals, interfaces, etc., as well as the software necessary for their operation. | Apple A5 APL2498 |
| Technological process Information about the technological process by which the chip is manufactured. Nanometers measure half the distance between elements in the processor. | 32 nm (nanometers) |
| Processor (CPU) The primary function of a mobile device's processor (CPU) is to interpret and execute instructions contained in software applications. | ARM Cortex-A9 |
| Processor size The size (in bits) of a processor is determined by the size (in bits) of the registers, address buses, and data buses. 64-bit processors have higher performance compared to 32-bit processors, which in turn are more powerful than 16-bit processors. | 32 bit |
| Instruction Set Architecture Instructions are commands with which the software sets/controls the operation of the processor. Information about the instruction set (ISA) that the processor can execute. | ARMv7 |
| Level 1 cache (L1) Cache memory is used by the processor to reduce access time to more frequently used data and instructions. L1 (level 1) cache is small in size and works much faster than both system memory and other cache levels. If the processor does not find the requested data in L1, it continues to look for it in the L2 cache. On some processors, this search is performed simultaneously in L1 and L2. | 32 kB + 32 kB (kilobytes) |
| Level 2 cache (L2) L2 (level 2) cache is slower than L1 cache, but in return it has a higher capacity, allowing it to cache more data. It, like L1, is much faster than system memory (RAM). If the processor does not find the requested data in L2, it continues to look for it in the L3 cache (if available) or in RAM memory. | 1024 kB (kilobytes) 1 MB (megabytes) |
| Number of processor cores The processor core executes software instructions. There are processors with one, two or more cores. Having more cores increases performance by allowing multiple instructions to be executed in parallel. | 2 |
| CPU clock speed The clock speed of a processor describes its speed in terms of cycles per second. It is measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). | 1000 MHz (megahertz) |
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) handles calculations for various 2D/3D graphics applications. In mobile devices, it is most often used by games, consumer interfaces, video applications, etc. | PowerVR SGX543 MP2 |
| Number of GPU cores Like a CPU, a GPU is made up of several working parts called cores. They handle graphics calculations for various applications. | 2 |
| Amount of random access memory (RAM) Random access memory (RAM) is used by the operating system and all installed applications. Data stored in RAM is lost after the device is turned off or restarted. | 512 MB (megabytes) |
| Type of random access memory (RAM) Information about the type of random access memory (RAM) used by the device. | LPDDR2 |
Built-in memory
Each mobile device has built-in (non-removable) memory with a fixed capacity.
Screen
The screen of a mobile device is characterized by its technology, resolution, pixel density, diagonal length, color depth, etc.
| Type/technology One of the main characteristics of the screen is the technology by which it is made and on which the quality of the information image directly depends. | IPS |
| Diagonal For mobile devices, screen size is expressed by the length of its diagonal, measured in inches. | 7.9 in (inches) 200.66 mm (millimeters) 20.07 cm (centimeters) |
| Width Approximate screen width | 6.32 in (inches) 160.53 mm (millimeters) 16.05 cm (centimeters) |
| Height Approximate screen height | 4.74 in (inches) 120.4 mm (millimeters) 12.04 cm (centimeters) |
| Aspect Ratio The ratio of the dimensions of the long side of the screen to its short side | 1.333:1 4:3 |
| Permission Screen resolution shows the number of pixels vertically and horizontally on the screen. Higher resolution means clearer image detail. | 1024 x 768 pixels |
| Pixel Density Information about the number of pixels per centimeter or inch of the screen. Higher density allows information to be displayed on the screen with clearer detail. | 162 ppi (pixels per inch) 63 ppcm (pixels per centimeter) |
| Color depth Screen color depth reflects the total number of bits used for color components in one pixel. Information about the maximum number of colors that the screen can display. | 24 bit 16777216 flowers |
| Screen area Approximate percentage of screen area occupied by the screen on the front of the device. | 71.97% (percent) |
| Other characteristics Information about other screen features and characteristics. | Capacitive Multi-touch |
| LED-backlit Oleophobic (lipophobic) coating |
Sensors
Different sensors perform different quantitative measurements and convert physical indicators into signals that a mobile device can recognize.
Rear camera
The main camera of a mobile device is usually located on its back panel and may be combined with one or more secondary cameras.
| Image Resolution One of the main characteristics of cameras is resolution. It represents the number of horizontal and vertical pixels in an image. For convenience, smartphone manufacturers often list resolution in megapixels, indicating the approximate number of pixels in millions. | 2592 x 1944 pixels 5.04 MP (megapixels) |
| Video resolution Information about the maximum video resolution that the camera can record. | 1920 x 1080 pixels 2.07 MP (megapixels) |
| Video recording speed (frame rate) Information about the maximum recording speed (frames per second, fps) supported by the camera at maximum resolution. Some of the most basic video recording speeds are 24 fps, 25 fps, 30 fps, 60 fps. | 30fps (frames per second) |
| Characteristics Information about additional software and hardware features of the rear (rear) camera. | Geographical tags Touch Focus Face recognition |
Front-camera
Smartphones have one or more front cameras of various designs - a pop-up camera, a rotating camera, a cutout or hole in the display, an under-display camera.
Audio
Information about the type of speakers and audio technologies supported by the device.
Radio
The radio of the mobile device is a built-in FM receiver.
Location determination
Information about the navigation and location technologies supported by your device.
WiFi
Wi-Fi is a technology that provides wireless communication for transmitting data over close distances between various devices.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a standard for secure wireless data transfer between various devices of different types over short distances.
USB
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an industry standard that allows different electronic devices to exchange data.
Headphone jack
This is an audio connector, also called an audio jack. The most widely used standard in mobile devices is the 3.5mm headphone jack.
Connecting devices
Information about other important connection technologies supported by your device.
Browser
A web browser is a software application for accessing and viewing information on the Internet.
Video file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support different video file formats and codecs, which respectively store and encode/decode digital video data.
Battery
Mobile device batteries differ from each other in their capacity and technology. They provide the electrical charge necessary for their functioning.
Specific Absorption Rate (SAR)
The SAR level refers to the amount of electromagnetic radiation absorbed by the human body while using a mobile device.
| Body SAR level (EU) The SAR level indicates the maximum amount of electromagnetic radiation to which the human body is exposed when holding a mobile device at hip level. The maximum permissible SAR value for mobile devices in Europe is 2 W/kg per 10 grams of human tissue. This standard has been established by the CENELEC Committee in compliance with the ICNIRP 1998 guidelines and IEC standards. | 1 W/kg (Watt per kilogram) |
| Body SAR level (US) The SAR level indicates the maximum amount of electromagnetic radiation to which the human body is exposed when holding a mobile device at hip level. The highest permissible SAR value in the USA is 1.6 W/kg per 1 gram of human tissue. This value is set by the FCC, and the CTIA monitors mobile devices' compliance with this standard. | 1.19 W/kg (Watt per kilogram) |
The leader among compact tablets
With a slight delay after the start of global sales of the iPad Air, the second new Apple product presented on October 22 - the iPad mini with Retina display - became available to customers. Being, perhaps, one of the most anticipated devices of this year, the iPad mini went on sale in Russia at the same time as the whole world, which is very rare. True, the official online store indicates a delivery time of 2-3 weeks, but this did not stop us from quickly getting hold of the new product for testing.
Since all the general information about the iPad mini with Retina display has already been given in the report from the Apple presentation, we will not repeat it. Let us only note that this is the first update to the iPad mini, and it is all the more important that Apple not only updated the “internals” of the device, but also equipped it with a screen of a fundamentally higher level.
- Apple A7 SoC @1.3 GHz (2 cores, 64-bit Cyclone architecture based on ARMv8)
- GPU PowerVR G6430
- Apple M7 motion coprocessor including accelerometer, gyroscope and compass
- RAM 1 GB
- Flash memory from 16 to 128 GB
- No memory card support
- Operating system iOS 7.0
- Touch display IPS, 7.9″, 2048×1536 (326 ppi), capacitive, multi-touch
- Cameras: front (1.2 MP, 720p video via FaceTime) and rear (5 MP, 1080p video)
- Wi-Fi 802.11b/g/n (2.4 and 5 GHz; MIMO support)
- Cellular (optional): UMTS/HSPA/HSPA+/DC-HSDPA (850, 900, 1700/2100, 1900, 2100 MHz); GSM/EDGE (850, 900, 1800, 1900 MHz), LTE Bands 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 13, 17, 18, 19, 20, 25, 26
- Bluetooth 4.0
- 3.5mm stereo headset jack, Lightning dock connector
- Lithium polymer battery 24.3 Wh
- A-GPS (version with cellular module)
- Dimensions 200×134.7×7.5 mm
- Weight 331 g (our measurement)
Let's compare the iPad mini Retina to its main competitor, the 2013 Google Nexus 7, as well as the first-generation iPad mini and iPad Air.
| iPad mini with Retina display | iPad Air | iPad mini first generation | Google Nexus 7 2013 | |
| Screen | IPS, 7.9″, 2048×1536 (326 ppi) | IPS, 9.7″, 2048×1536 (264 ppi) | IPS, 7.9″, 1024×768 (163 ppi) | IPS, 7″, 1920×1200 (323 ppi) |
| SoC (processor) | Apple A7 @1.3 GHz (2 cores, 64-bit Cyclone architecture based on ARMv8) + M7 coprocessor | Apple A7 @1.4 GHz (2 cores, 64-bit Cyclone architecture based on ARMv8) + M7 coprocessor | Apple A5 @1 GHz (2 cores, ARM Cortex-A9) | Qualcomm Snapdragon S4 Pro @1.5 GHz (4 Krait cores) |
| GPU | PowerVR G6430 | PowerVR G6430 | PowerVR SGX543MP2 (2 cores, 200 MHz each) | Adreno 320 |
| Flash memory | from 16 to 128 GB | from 16 to 128 GB | from 16 to 64 GB | 16/32 GB |
| Connectors | Lightning dock connector, 3.5mm headphone jack | Lightning dock connector, 3.5mm headphone jack | Micro-USB, 3.5 mm headphone jack | |
| Memory card support | No | No | No | No |
| RAM | 1 GB | 1 GB | 512 MB | 2 GB |
| Cameras | front (1.2 MP, 720p video via FaceTime) and rear (5 MP, 1080p video shooting) | front (1.2 MP, support for video communication 720p) and rear (5 MP, video recording 1080p) | front (1.2 MP) and rear (5 MP, 1080p video shooting) | |
| Internet | Wi-Fi (optional - 3G, as well as 4G/LTE) | Wi-Fi (optional - 3G and LTE) | ||
| Battery capacity (mAh) | 6471 | 8820 | 4440 | 3950 |
| operating system | Apple iOS 7.0 | Apple iOS 7.0 | Apple iOS 6.0 (upgrade to iOS 7.0 available) | Google Android 4.3 |
| Dimensions (mm)* | 200×134×7.5 | 240×170×7.5 | 200×138×7.2 | 200×114×8.7 |
| Weight (g) | 339** | 480 | 311*** | 294 |
| average price | T-10546224 | T-10548616 | T-8485573 | T-10451398 |
*according to manufacturer information
** the weight of the version with a cellular module is indicated
*** the weight of the version without cellular module is indicated
**** for version with 16 GB flash memory and without cellular module
It is clearly seen that the iPad mini Retina is identical to the iPad Air in almost all characteristics (except for dimensions). And this is incredibly cool, because the first generation iPad mini, released simultaneously with the iPad 4, had the same characteristics as the iPad 2. That is, now the iPad mini line has made a leap through two generations!
As for the comparison with Google Nexus 7, it is difficult to draw clear conclusions from the data presented in the table. However, it is significant that Google's tablet is slightly lighter and more compact than the iPad mini Retina. But at the same time it has a smaller screen and a plastic body.
Interestingly, despite the appearance of the new iPad mini, the previous model also remains in the company’s lineup, and its cost starts from 12 thousand rubles (which is 4 thousand less than the iPad mini Retina). In our article we will also try to answer the question of how much the difference between the two iPad minis is adequate to the amount of 4,000 rubles and how relevant the first iPad mini is today.
Packaging and equipment
The packaging of the iPad mini Retina is practically no different from the packaging of the previous generation tablet.

As for the packaging, everything here is also similar to the first iPad mini: leaflets, charger (5.1 V 2.1 A), Lightning cable, stickers and a key for removing the SIM card cradle (in the version with a cellular module).

Design
If the update of the large iPad affected, first of all, the design, then the appearance of the iPad mini remained practically unchanged.

The all-metal body (made of anodized aluminum) pleases with both appearance and functionality, and the frames around the screen even today, a year after the release of the first iPad mini, seem quite thin.

All buttons are metal and can be pressed with little effort. Their location is similar to the previous model. Top right is the Power button, top left is a 3.5 mm headphone jack. At the top center is the hole for the built-in microphone. On the right side there is a screen auto-rotate lock lever and a volume rocker.

On the model with a cellular module, there is a plastic insert at the top that hides the antenna. It, of course, somewhat spoils the overall appearance, but does not dampen the signal.

The main difference between the new iPad mini and the old one is the increased weight (by more than 20 grams) and thickness (by 0.3 mm). Visually they are the same. The photo above shows two iPad minis of different generations. But if the difference in thickness is really not visible, then the changed mass is already noticeable. However, this is quite acceptable, and these changes do not have a fundamental impact on the user experience.
Screen
The main feature of the new iPad mini is its Retina display with a resolution of 2048x1536. When testing the first iPad mini, which had a resolution of 1024x768, we noted the lack of a Retina display as its main disadvantage. And now Apple has solved the problem. True, today you won’t surprise anyone with screens with such a density of dots per inch, so other characteristics come to the fore, which, as a rule, are not indicated in official technical specifications and are revealed only through careful testing.
A detailed examination of the new Retina screen was carried out by the editor of the “Projectors and TV” section, Alexey Kudryavtsev.
The front surface of the screen is made in the form of a glass plate with a mirror-smooth surface that is scratch-resistant. Judging by the reflection of objects, there is a very effective anti-glare filter, approximately equal in reducing the brightness of the reflection to the screen filter of the Google Nexus 7 2013 (we will compare it with it below). For clarity, here are photographs in which a white surface is reflected in the turned off tablet screens (from left to right: Nexus 7, iPad mini with Retina display and old iPad mini):
Visually, the brightness of the reflection is difficult to assess due to differences in color tone and frame color, but statistics from the graphics editor show that the screen on the new iPad mini is slightly lighter (average brightness value is 95) than that of the Nexus 7 (83), and darker than the old iPad mini (108).
The reflection in the screen triples, which suggests the presence of an air gap between the surface of the matrix and the outer glass. From the point of view of image perception, this is a minus, but a screen with a separate outer glass (also known as a touch panel) is easier and cheaper to repair. The outer surface of the screen has a special oleophobic (grease-repellent) coating (effective, but still worse than that of the Nexus 7), so fingerprints are removed much more easily and appear at a slower rate than with regular glass.
With manual brightness control, its maximum value was about 410 cd/m², and the minimum was 8 cd/m². The maximum value is quite high, and, given the good anti-glare properties of the screen, the image on the screen should be clearly visible in bright daylight. In complete darkness, the brightness can be reduced to a comfortable level. Automatic brightness adjustment works based on the light sensor (it is located to the left of the front camera eye). In this case, the brightness can only automatically increase - when the level of external illumination decreases, we did not wait for a corresponding decrease in screen brightness. However, if you put the tablet into sleep mode and turn it back on, the brightness will be set in accordance with external conditions. The minimum and average levels in Auto mode depend on the initial position of the brightness adjustment slider. So, when the slider is set to maximum, automatic adjustment does not work - the brightness remains maximum regardless of external conditions. If the slider is approximately in the middle of the scale, then in bright light (corresponding to lighting on a clear day outdoors, but without direct sunlight - 20,000 lux or a little more) the maximum brightness is 410 cd/m², in an office illuminated by artificial light (approximately 400 lux ) - 200 cd/m² (normal), in the dark - 150 cd/m² (too much). If the slider is at a minimum, then under the above conditions the values are as follows: 410, 70, 8 cd/m². Thus, this function works adequately at some average and slightly below average brightness adjustment positions. At the extreme initial positions of the slider, the brightness is either always maximum, or decreases too much in the dark. At any brightness level, there is virtually no backlight modulation, so there is no screen flickering.
This tablet uses an IPS matrix. The microphotographs show a typical IPS subpixel structure:
The screen has good viewing angles without inverting shades and without significant color shifts, even with large viewing deviations from perpendicular to the screen. For comparison, here are photos in which the same images are displayed on the screens of the Nexus 7 (pictured above) and the new iPad mini (bottom), with the brightness of both screens set to approximately 200 cd/m². Picture perpendicular to the screens:
And a white field under the same conditions:
Now at an angle of approximately 45 degrees to the plane and to the side of the screen:
It can be seen that the colors did not “float” on both tablets.
And a white field at an angle:
The brightness at an angle for both tablets decreased equally (about four times, based on the difference in shutter speed), but the color tone did not change much.
When deviated diagonally, the black field is lightened weakly and acquires a red-violet tint or remains almost neutral gray. A photo from the Nexus 7 shows this for comparison (the brightness of both tablets is the same!):
And along the other diagonal:
It can be seen that the new iPad mini has a different color tone of the black field depending on the diagonal, but its brightness is the same or slightly lower than the black brightness of the Nexus 7 at the same angle.
When viewed from a perpendicular perspective, the uniformity of the black field is very good, since in fact only along one edge one can see some hints of areas with increased brightness of the black field:
The Google Nexus 7's black uniformity is worse, but it has better black depth in the center of the screen. Indeed, the contrast (approximately in the center of the screen) of the new iPad mini is not the highest - about 790:1. The response time for the black-white-black transition is 22 ms (13 ms on + 9 ms off). The transition between halftones of gray 25% and 75% (based on the numerical value of the color) and back takes a total of 34 ms. The gamma curve constructed using 32 points did not reveal a blockage either in the highlights or in the shadows, and the index of the approximating power function turned out to be 2.22, which is not significantly higher than the standard value of 2.2, while the real gamma curve deviates little from the power-law dependence:
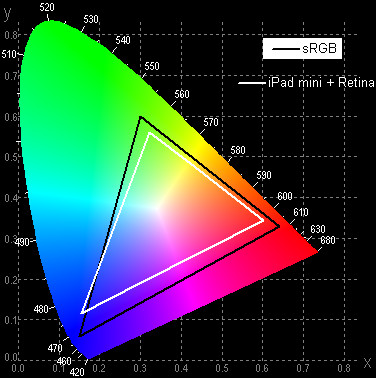
The color gamut is noticeably narrower than sRGB:
Apparently, the matrix’s light filters mix the components with each other, and the spectra confirm this. This technique allows you to increase the brightness of the screen with the same energy consumption for backlighting. As a result, the colors of images - drawings, photographs and films - oriented to the sRGB space (and these are the vast majority) have a slightly reduced saturation. You can't tell from the photos above, as the camera slightly increases the color saturation.
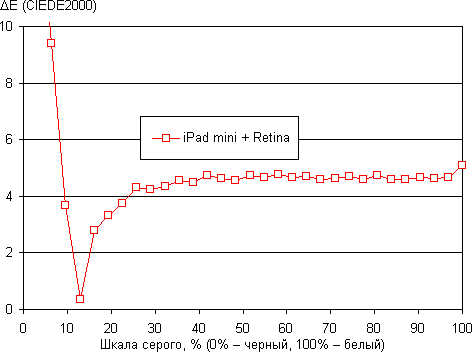
The balance of shades on the gray scale is very good, since the color temperature is close to the standard 6500 K and the deviation from the blackbody spectrum (delta E) is significantly less than 10, which is considered an acceptable indicator for a consumer device. At the same time, the variation in color temperature and delta E is small, which also has a positive effect on the visual perception of color balance. (Dark areas of the gray scale can be ignored, since color balance there is not very important, and the error in measuring color characteristics at low brightness is large.)
The range of brightness adjustment for the iPad mini Retina screen is quite wide, and the anti-glare filter is very effective, which allows you to comfortably use the tablet both on a sunny summer day outside and in complete darkness. There is automatic brightness adjustment, and it works more or less adequately, but only up, which will force the user to either set the brightness manually, or force the brightness to decrease, putting the tablet into sleep mode and turning it back on. However, all Apple tablet users are probably already accustomed to this feature. The advantages of the screen include an effective oleophobic coating, a standard gamma curve, very good color balance and excellent black stability to deviation of the gaze from perpendicular to the screen surface, as well as excellent black field uniformity. It was strange to discover that the color gamut is still less than sRGB, but this tablet must have at least one drawback!..
In terms of software, the iPad mini Retina has nothing fundamentally new except for the fact that it is sold with pre-installed iOS 7, while the previous model left the factories with iOS 6. But it can also be updated to iOS 7. We also note that users iPad mini Retina offers popular Apple apps such as Pages, Numbers, Keynote, and GarageBand for free.
Performance
Like the iPhone 5s and iPad Air, the iPad mini Retina runs on Apple's new A7 SoC. In the articles on the links provided, we talked in detail about this SoC, so we won’t repeat ourselves and go straight to the tests. We were also interested in what the difference is between the two iPad minis with iOS 7.0.4 installed on both devices. That is why the test results below may differ from the results that were published in the article about the first iPad mini, since the benchmarks have since been updated and a new version of the OS has been released.
Let's start with browser tests: SunSpider 1.0, Octane Benchmark and Kraken Benchmark. In all cases, we used the Safari browser from iOS 7 on Apple devices, and Google Chrome on Android.
The results are interesting. The new iPad mini is about four (!!!) times faster than the first generation iPad mini, but at the same time is slightly behind the iPad Air, although it runs on the same SoC. It can be assumed that the SoC in the iPad mini Retina regulates the energy saving process a little differently and, for certain tasks, slightly reduces the CPU frequency. But, we emphasize, this is only an assumption. But the main Android competitors remained far behind the iPad mini Retina (although, of course, they overtook the first iPad mini).
In Geekbench 3 - a multi-platform benchmark that measures CPU and RAM performance - the situation repeated itself.
The layout is the same as in browser tests. And this indicates that the results are indeed correct.
Now let's look at the GPU performance. There are two multi-platform benchmarks available here: GFXBench (formerly GLBenchmark 2.7) and 3DMark. Let's start with the GFXBench results.
| Apple iPad mini second generation (Apple A7) | Apple iPad mini first generation (Apple A5) | Apple iPad Air (Apple A7) | Google Nexus 7 2013 (Qualcomm Snapdragon S4 Pro) | LG G Pad 8.3 (Qualcomm Snapdragon 600) |
|
| GFXBench 2.7.2 T-Rex HD (C24Z16 Offscreen) | 27 fps | 3.4 fps | 27 fps | 15 fps | 14 fps |
| GFXBench 2.7.2 T-Rex HD (C24Z16 Onscreen) | 21 fps | 6.4 fps | 21 fps | 15 fps | 13 fps |
| GFXBench 2.7.2 T-Rex HD (C24Z16 Offscreen Fixed Timestep) | 25 fps | 3.5 fps | 25 fps | 14 fps | 13 fps |
| GFXBench 2.7.2 T-Rex HD (C24Z16 Onscreen Fixed Timestep) | 20 fps | 6.9 fps | 20 fps | 14 fps | 13 fps |
| GFXBench 2.7.2 Egypt HD (C24Z16) | 63 fps | 15 fps | 63 fps | 39 fps | 35 fps |
| GFXBench 2.7.2 Egypt HD (C24Z16 Offscreen) | 49 fps | 22 fps | 49 fps | 30 fps | 35 fps |
And again we see the same picture, with the only difference that now the results of both devices on the Apple A7 are exactly identical.
Here again you can see a slight loss of the iPad mini Retina to its older comrade. But what's more striking is the difference between the two generations of iPad mini. I can’t believe that these devices are only one year apart! However, the gap from Android tablets is also significant.
Thus, the iPad mini with Retina display is the most productive modern tablet in the mid-price segment. If you love playing 3D games and want a device that can be updated at least twice to a new version of the operating system, you can safely buy the iPad mini Retina. But the previous generation iPad mini is no longer relevant today, since for the same money (about 12 thousand rubles) you can buy a much more productive Android tablet with a Full HD screen.
Autonomous operation
If we knew the approximate level of performance in advance (since we had already tested solutions on the Apple A7 SoC), then the situation with autonomous operation created a real intrigue. After all, now the device needs to display an image with twice the higher resolution, but the body dimensions remain the same, so the battery cannot be greatly increased. This raised natural concerns that the new iPad mini would be inferior to its predecessor in terms of battery life.
However, as tests showed, these fears were in vain. The battery life not only did not decrease, but even increased slightly. Here, however, it is worth making a reservation that for this comparison we tested the first generation iPad mini on the latest version of the operating system - iOS 7.0.4. It is possible that on the original iOS 6 with which it was released, the result would have been a little better. But even in the current version, this is a decent operating time - for both iPad minis.
The results are presented in the table.
Interestingly, the sensational result of the 2013 Google Nexus 7, obtained in reading mode, could not be surpassed by the new iPad mini. In general, all other devices are like the Moon. But in the other two modes, the iPad mini Retina outperforms both Android competitors.
We also note that under load, the new iPad mini heats up more than its predecessor, in which the heating is almost not felt.
Camera
iPad Air is equipped with two cameras - front with a resolution of 1.2 megapixels and rear with a resolution of 5 megapixels, similar to the cameras of the first iPad mini and iPad Air. Since the iPad mini is much more suitable for shooting than the larger iPad, we decided to do a full test using our smartphone camera testing methodology, and at the same time compare the new product in terms of camera quality with the first generation iPad mini and iPad Air. Photography and commentary were done by Anton Soloviev.
iPad mini Retina | |
 |  |
Good dynamic range and well-processed noise. |
|
 |  |
The sharpness is not bad, but the lack of any stabilization noticeably affects it. |
|
 |  |
The sharpness is quite good; if you wish, you can make out the license plate of the nearest car. |
|
 |  |
There is noticeable blur in the corners of the frame, although the upper central part is quite sharp. |
|
 |  |
The number plate of the nearest car is clearly visible. |
|
 |  |
At shorter shutter speeds the situation improves noticeably. Sharpness is uniform across almost the entire frame. |
|
 |  |
In such scenes, the camera chooses exposure well. |
|
 |  |
The camera is relatively good at macro photography in low light. |
|
We can say that the shooting quality of the iPad mini Retina camera has not changed noticeably compared to the iPad mini. Minor improvements have only been made to noise processing: the algorithm for the noise reduction has remained almost unchanged, but visually its work has become softer, and due to this, small details are better processed in the pictures. However, the camera is still afraid of noise and tries to work at minimum photosensitivity values, compensating for exposure at the expense of shutter speed, so in low light there is a high probability of blur due to relatively long shutter speeds. As it turns out, relatively long shutter speeds in this case are values from 1/40 of a second and higher, since the iPad mini Retina camera does not have any stabilization system. For example, almost all of the above photographs were taken under identical conditions, each in triplicate, and in almost all cases, two out of three photographs were blurred.


Lighting

As can be seen from the graph, in terms of relative resolution, the iPad mini Retina camera is not so far behind the iPad mini camera and has almost caught up with the iPad Air camera. However, after a detailed examination of the photos of the stand, it becomes clear that the iPad mini Retina is still a significant step forward compared to the iPad mini. It's also worth noting that the camera's angle of view has become slightly smaller, despite the same nominal focal length indicated in EXIF. Even though the camera hasn't changed much, it now looks refined. There are still some points that I would like to improve, but these are, rather, purely software limitations.
Among the characteristic features of the camera, we can highlight good noise reduction, good and fairly uniform sharpness across the plans and across the field, and a reasonable choice of exposure.
Overall, the camera's image quality is decent, especially for a tablet, despite the low resolution. The camera probably has no obvious shortcomings, but the lack of a flash significantly limits its scope of use. However, it is quite suitable for artistic or documentary photography in appropriate lighting.
conclusions
The previous iPad mini evoked mixed emotions: the form factor seemed interesting (the screen is larger than 7 inches, but the body can be grasped with one hand in a vertical orientation), but the low resolution of the display spoiled the whole impression. This was especially noticeable if you were using a larger iPad with a Retina display. After that, working with the iPad mini was simply physically uncomfortable.
And now Apple has released the second version of the iPad mini - and here it not only corrected the situation with screen resolution, but also radically increased the performance of the device. The price remained quite attractive, and the battery life and dimensions remained virtually unchanged.
Thus, the choice is no longer between “large and modern device” and “compact but outdated”. Now you have to choose exclusively between two screen diagonals and, accordingly, the dimensions of the tablet (which, however, does not affect the thickness). If you prefer a more compact format, plan to regularly take the tablet with you on trips, or use it in transport, then you can safely take the iPad mini Retina. It is a little more expensive than Android tablets of a similar form factor, but it is significantly better in performance.
In our opinion, the more likely competitors of the iPad mini Retina are not even tablets of a compact form factor, but tablet phones - Sony Xperia Z Ultra, Samsung Galaxy Note 3, etc. In terms of performance, they are approximately on the same level as the iPad mini Retina, and in terms of screen quality are not inferior (and even superior in terms of pixel density per inch), but they can be used both as a tablet and as a smartphone. True, the cost of top-end tablet phones is significantly higher than that of the iPad mini, but the screen is still smaller. Therefore, the Apple product has its own specific niche, different from both tablet phones and compact Android tablets.
Overall, we definitely recommend purchasing the iPad mini with Retina display, unless you have already bought an iPad Air (or are not planning to do so). But the first generation iPad mini seems to us to be an acceptable option only if the buyer wants to get an Apple tablet as cheaply as possible, and the rest doesn’t matter. If possible, then, of course, it’s worth paying an additional 4,000 rubles and getting a fundamentally more modern device. And, by the way, owners of the first generation iPad mini can also safely go to stores for a new iPad mini, if their financial capabilities allow it. The update will not be superfluous at all.
In conclusion of the article, we bring to your attention our video review of the Apple iPad mini tablet with Retina display:
| 16 GB (+3G) | 32 GB (+3G) | 64 GB (+3G) | 128 GB (+3G) |
| Average price according to Yandex.Market | |||
| T-10546224 (T-10546225) | T-10546226 (T-10546227) | T-10546228 (T-10546229) | T-10548766 (T-10548769) |
| iPad mini Retina 16 GB (+3G) offers according to Yandex.Market | |||
| L-10546224-5 | L-10546225-5 | ||
| iPad mini Retina 32 GB (+3G) offers according to Yandex.Market | |||
| L-10546226-5 | L-10546227-5 | ||
| iPad mini Retina 64 GB (+3G) offers according to Yandex.Market | |||
| L-10546228-5 | L-10546229-5 | ||
| iPad mini Retina 128 GB (+3G) offers according to Yandex.Market | |||
| L-10548766-5 | L-10548769-5 | ||
Advantages of the tablet:
Good screen, responds quickly. Good LTE speed. The case is very pleasant to the touch, not easily soiled, and has not been scratched in 3 months. Good camera for a tablet, both front and back. The battery life is excellent, after my Samsung Galaxy Note 10.1 from a year and a half ago - it’s just a miracle. You can really forget about charging for the whole day. It also charges quickly (~1 hour 20 minutes). I like the design of the new iOS more than the old one.
A large number of accessories.
I really like Smart Cover, it's time other manufacturers do something similar.
Apple's stupidity with downloading files from the Internet, but at the same time there is a plus - it does not download third-party virus programs from the Internet. Anyone who uses Android will understand me.
Disadvantages of the tablet:
From a design point of view, the screen bends a little. In the spirit of the Chinese, it’s made of plastic, but I have a perfect device, so we’ll assume that it’s intended that way. On the subway, he constantly loses connection when switching from station to station. For it to find the signal again, you need to turn off/on the Internet. But you won’t be able to do this quickly, because in a perfect tablet this is done from the menu. And you are in an ideal tablet, a device for 30 thousand, every time you look for it in the settings. This is very annoying, because Android devices work great in this regard.
Then everything is just about iOS itself.
The keyboard is uncomfortable and impossible to customize. You need to press the symbol button to call up the comma and period. It wastes time. But I liked the autocorrect function, it’s convenient.
In general, it’s difficult to customize everything for yourself, especially after Android.
I did a Jailbreak - it’s so hard to find tweaks that will help you work with the tablet like on Android. But at least it somehow made the work easier.
IOS is completely unsuitable for studying, you will not be able to NORMALLY transfer files, work with different formats and archives, edit files, open them where you want, customize the device for yourself, etc. If you want to do something more than watch a movie, be so kind as to either sit at your computer with crappy iTunes, or use 3-5 cloud storages for at least more or less convenient work. And yes, you won’t be able to send the file normally either, everywhere you need some kind of dancing with a tambourine.
Comment about the tablet:
I chose a tablet in early January. I really didn’t want to buy Apple because it was on Android from the very beginning, but I couldn’t find any analogues. Galaxy Note 10.1 2014 edition is very sluggish and inconvenient; Samsung failed to create a good device for the second time. Sony didn't consider it at all. The Chinese, of course, also gave up. Why not Mini? Because I’m used to large screens, although the small iPad is really good, I’m an Android lover and I’ll say right away that no Nexus or Tab can compare with it.
Yes, the Air tablet is good, everything is beautiful and cool, but not Android. It's inconvenient at some points. I want more convenience from the device and less steps to configure, but here everything is exactly the opposite. Starting from registering an Apple ID to optimizing and connecting various functions. If you, like me, decide to try iOS, be prepared for shouting, swearing and misunderstanding of logic. Yes, of course, some solutions are implemented in an interesting way and work better (notifications, for example), but this is only a small part. Basically, everything is configured through a certain place and with great difficulties.
Don't expect miracles - everything crashes the same way. Moreover, the application may crash, worse when it starts to reboot by itself. I chalked it up to Jailbreak.
I'm lucky - I don't use the completely stupid iTunes program. And this is another problem that you simply cannot open the device in the file manager and view all the files. And you can only connect 5 computers.
Really pleased with the screen and body. It's just nice to hold and use. But even now this will not surprise anyone, the same Samsung made a very cool screen with a rather nice body.
Bottom line: if you have been using Android all your life and you need something more than a device for 30 thousand to use the camera and surf VK - think carefully about whether you need it or not. True, a very different hemorrhoid.
As an alternative - Note Pro, you can look at Sony.
I think I’ll go back when they release something decent from normal materials on Android.