Basic elements of the graphical user interface of Windows OS Sklyarova T.G. computer science teacher at the technological lyceum
Subject : "Graphic Windows interface».
Teacher: Erokhina E.V.
Lesson objectives:
- introduce the concept of a graphical interface, the purpose of Windows controls, program window elements, the purpose of the left and right buttons of a mouse-type manipulator.
- to cultivate students’ information culture, attentiveness, accuracy, discipline, perseverance.
- develop cognitive interests, logical thinking, mouse skills, self-control, and the ability to write a supporting note.
Implement the principle of visibility
Use all three types of memory when filling out the supporting notes.
Increase interest in the subject using ICT.
Equipment:
computer, projector, computer presentation, handouts for reference notes.
During the classes:
1. Org. moment.
Greetings, checking those present. Explanation of the lesson.
2. Warm up
We begin each lesson with a short warm-up, which not only helps develop your logical thinking, but allows me to check how you have mastered the material from the previous lesson.
Please look at the screen and guess which words are encoded?
Now let's see how well you know the parts of some whole concept.
Currently, all operating systems for personal computers provide user interaction using a graphical interface.
This allows even a novice computer user to work confidently in the operating system environment (perform file operations, run programs, and so on).
In this lesson we will look at how to manage this most important and complex program, i.e. Windows OS.
3. Theoretical part.
What is a graphical interface? This is an opportunity that allows human interaction with a computer in the form of a dialogue using windows, menus and controls (dialog bars, buttons, and so on). All these objects are presented in the pictures.
Most often, the user has to work with dialog panels, which include various tabs. Left-clicking will help you navigate through them and work with various controls. Let's get to know them:
Button with an inscription indicating some action allows you to perform it by clicking the left mouse button
Text field allows you to enter a certain sequence of characters
Drop-down list represents a set of values. How is it different from a text field?
Checkbox assigns a value to some parameter. Which distinctive feature at the flag?
Switch allows you to select only one option, excluding others. What is he?
Counter allows you to increase or decrease the value of a field using the two arrow buttons located in it
Slider allows you to smoothly change the value various parameters. You will try to find it yourself on the next slide.
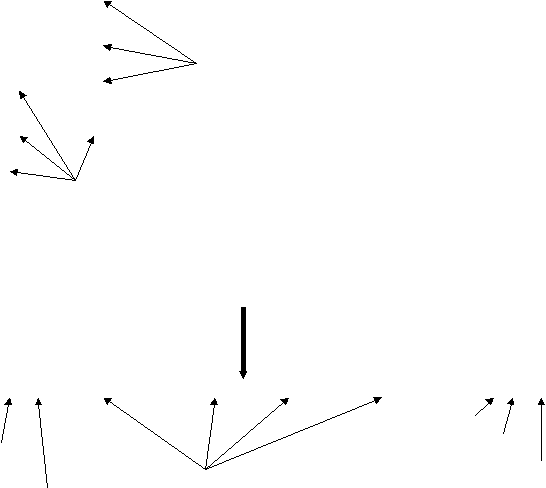
Here is the first part of the reference summary, which is called “Windows Controls”. Let's fill it with the captions under the arrows of the first picture. Let's start with the bottom right arrow and then go clockwise. Who will name the first control element?
And in the second picture we ourselves will mark with arrows the tabs of the dialog panels and the slider. Who will show the tabs and the slider?
The Windows interface is simple and accessible, and almost everyone can solve almost all of its riddles.
To work with the graphical interface, a mouse or other coordinate input device is used. What manipulations should the user be able to perform:
left click - pressing and releasing the main (usually left) mouse button once;
right click - pressing and releasing an additional (usually right) mouse button once;
double click - two clicks of the main mouse button with a minimum time interval between them;
dragging (dragging) - pressing the left or right mouse button and moving an object with the button pressed.
Let us together try to list the capabilities of each of the buttons of a mouse-type manipulator and note them in the second part of the supporting summary.
A user working on a computer calls various programs, creates and edits files, organizes them through directories. Files available to the user are its information space.
Try to find the answer to this question in the textbook on pages 66-67: How can a user configure his information space? This paragraph talks about operating system objects such as the Desktop and shortcuts. Let's get acquainted with these concepts?
Windows GUI Elements:
Desktop.
The name “Desktop” was chosen well. On it, like on a regular desktop, there are various programs and tools presented in the form of icons or icons.
Icons.
Icons in Windows represent programs and documents. Launch is in progress double by clicking the mouse button on the icon. The program can be located directly on the Desktop, or it can be hidden deep on the disk, but even in this case it is presented on the Desktop in its own way - a shortcut.
Labels.
A program shortcut is not the program itself, but only its image, an indication of the place on the disk where it is located. Double Clicking the shortcut also launches the program. Labels differ from icons by having a small arrow at the bottom left.
Task bar.
Located at the bottom of the screen. It contains: the Start button, buttons for open windows, indicators and a clock. (Mark on your supporting notes)
Window. (We will study in the next lesson and fill out the rest of the supporting notes)
A window is one of the main elements of the Windows interface. A window is a framed portion of the screen that displays an application, document, or message. Let's look at the elements of the window and fill in the corresponding part of the supporting outline.
Thus, we have clearly become acquainted with the elements that allow us to establish a dialogue between the Windows operating system and the user. We filled out a basic summary that will help you better remember the Windows controls, the purpose of the mouse buttons, elements of the Desktop and windows.
4. Homework
At home, you will refer to it again, and also analyze:
§ 2.5 -2.6, complete task 2.13 and prepare for practical work No. 7 (p. 150)
5. Practical work and summing up the lesson.
Now let's do it practical work No. 6 from your textbook from page 148. At home you should have prepared for it. Get on the computers.
Look closely at the dialog panel digital clock.
Name the tabs present on this panel?
What controls are present on the Date and Time tab?
Using which element will you set the year you need?
Which element will you use to set the month?
On what day of the week were you born?
Do the second part yourself.
What is the time difference between Greenwich and Moscow?
What is the time difference between Greenwich and Yakutia?
What is the time difference between Moscow and Yakutia?
Well done. Thank you. Get your places in order. The lesson is over. Well done. Thank you. Get your place in order. Ouch?
BACKGROUND SUMMARY
Control elements

Basic Mouse Operations
LEFT MOUSE BUTTON
RIGHT MOUSE BUTTON
One click
drag and drop(dragging without releasing the button)
Desktop elements


Window elements

Municipal educational institution "Brilinskaya basic secondary school"
User interface
Computer science teacher Valery Nikolaevich Klenkov
Computer Science 7th grade

Let's repeat
1. What is a file?
2. What is a file system?
3. What does the file name consist of? What characters are not allowed in file names?
The following characters are not allowed in file names:
\ І / : * ? “
4 . What is a directory? What is the root directory? How is it designated?
For example, for hard drive C: the root directory is designated WITH: \

Let's repeat
5 . What is a file structure?
6. What is full name file? Write down the full file name Essay .doc
Cartoons
Presentations
Literature
Abstract.doc
F:\ School\Texts\Literature\Abstract .doc

- Get acquainted with the concept of “interface”.
- Consider the features of the graphical user interface.
- Get acquainted with the concept of “information space”.

Interface
The means that provide interconnection between objects of the “human-computer” system are called interface .
There are different interfaces:
- hardware (means of interaction between PC devices);
- program(means of interaction of programs with each other, as well as software and information resources);
- hardware-software (means of interaction between PC hardware and software);
- custom – means of human-computer interaction.
 copy letter_1.txt C:\RESEV – the command copies the file letter _1. txt from the C:\MYDOCS\LETTERS directory to the C:\RESERV directory." width="640"
copy letter_1.txt C:\RESEV – the command copies the file letter _1. txt from the C:\MYDOCS\LETTERS directory to the C:\RESERV directory." width="640" User interface
Historically the first was command line interface – the user entered all commands from the keyboard.
For example, C:\MYDOCS\LETTERS\copy letter_1.txt C:\RESEV
– team copies file letter _1. txt from the catalog C :\ MYDOCS \ LETTERS to the catalog C :\ RESERV .

User interface
Later, with the advent of the mouse, graphic interface – the user enters all commands by clicking the mouse on graphic objects shown on the screen.

User interface
Now in computer games and in virtual reality actively developing three-dimensional interface– for example, in a virtual museum or in computer game you can look around, come closer, move to another room.

object-oriented , because:
- objects are presented as icons:
- Objects are operated in the following windows:

GUI
Graphical interface is also called object-oriented , because:
- main element hardware control– manipulator:
Optical mouse
The first mouse invented by Douglas Engelbart
Modern mouse design

GUI
Graphical interface is also called object-oriented , because:
- main element program control– menu:

GUI
Icon My computer
Desktop – the main window of the graphical interface.
Icon My Documents
Icon Basket
Click on desktop objects
Icon network
Program shortcut Keyboard
Keyboard indicator
Task bar
Button Start

GUI
For two-way interaction (dialogue) between the computer and the user, dialog boxes .

GUI
Dialog boxes have a variety of controls:
List
Field input
Drop-down list
Checkbox
Slider
Switches
Counter
Complete task #125 on page 72 workbook

Information space
While working on a computer, the user generates information space – informational resources, available to the user when working on this computer.
To do this, the user:
- installs the software it needs on the computer;
- creates documents;
- copies documents or links from external media information and the Internet.

Homework
§ 2.5, No. 127 RT (crossword)
Correct answers 1. Software is a set of programs that make it possible to use a computer to solve different tasks. 2. System, application, instrumental 3. basic kernel, command processor, drivers, simple utilities application programs

Doс,.txt The file contains the program – executable file bmp,.jpg,.gif The file contains a Web page.avi The copy file.wav The file contains video information.bak The archive file.html,.htm The file contains graphic information.arj,.rar,.zip The file contains audio information.exe ,.com File contains text information


Labels and pictograms Icons with an arrow in the left corner, the so-called “shortcuts”. They are a reference, a pointer to an object. Copying or deleting does not cause corresponding actions on the object. Needed for quick access, created by the user. Icons without an arrow in the left corner are pictograms. Directly associated with an object, copying or deleting causes a corresponding action on the object. Automatically created for content and questions








CONTEXT MENUS OF OBJECTS allow you to familiarize yourself with the properties of an object (file, folder or disk), as well as perform permitted operations on it (copying, moving, deleting, etc.). To call the context menu, you need to right-click on the object icon to contents questions









Reinforcement Name the main elements of the Windows graphical interface. Explain the differences between shortcuts and icons.(answer)answer What can be located on the taskbar?.(answer)answer What is a window called in Windows? What types of windows do you know?.(answer)answer What elements do all windows have?. Name the elements inherent in folder and application windows..(answer)answer Name the elements dialog boxes. to questionsto contents

To use preview presentations create yourself an account ( account) Google and log in: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Windows GUI
Definition A graphical interface allows a person to interact with a computer in the form of a dialogue using windows, menus and controls (dialog bars, buttons, etc.).
Desktop Recycle Bin Network Neighborhood My Computer My Documents Icon Shortcuts
My Computer The My Computer icon on your desktop is a folder containing icons for all available disk drives (HDD, floppy disk etc.), as well as the Control Panel, the Printers folder and, in some cases, other folders. Desktop
My Documents The My Documents folder is a user’s personal folder in which it is customary, although not at all necessary, to store created documents, photographs, videos, etc. - that is, your personal files user. You can get to this folder: from the Start menu, from the My Computer folder, or from the desktop. Desktop
Recycle Bin The Recycle Bin folder temporarily stores deleted data. If necessary, you can restore the data and then delete it. Desktop
Labels/Icons. Shortcuts (with a small arrow in the lower left corner) and icons provide (by double clicking) fast access to drives, folders, documents, applications and devices. Desk 3
Taskbar Ru/En Clock Start Main menu
Start At the bottom of the screen there is a taskbar, on which there is a Start button, a button for running tasks and open folders and clock indicators. The Start button allows you to call up the Main Menu. Task bar
Main menu Provides access to almost all system resources and contains commands for launching applications, system settings, searching for files and documents, accessing help system etc. Taskbar
Clock At the far end of the taskbar is the Clock. Task bar
Ru/En By left clicking the mouse you can expand the indicator and switch to English layout, and with the right one - open the Properties dialog box and select the required combination of keystrokes on the keyboard to switch layouts. Task bar
Windows The most important element of the Windows graphical interface is windows. There are two main types of windows – application windows and document windows. Menu
Application windows Work area Borders Title Line horizontal menu Toolbar Buttons Windows
Workspace The inner part of a window that contains subfolders or document windows. Application windows
Borders A frame that encloses a window on four sides. The size of the window can be changed by moving the border with the mouse. Application windows
Title A line immediately below the top border of a window that contains the title of the window. Application windows
Icon system menu. The button on the left in the title bar opens a menu for moving and resizing the window. Application windows
Toolbar Located below the menu bar, it is a set of buttons that provides quick access to some commands. Application windows
Horizontal menu bar Located directly below the header, it contains menu items and provides access to commands. Application windows
The Minimize/Restore and Close buttons are located in the upper right part of the window. Application windows
Document windows Document windows are designed for working with documents and “live” inside application windows. You can expand, collapse, move, or resize these windows, but they always remain within their application window. Document windows have the same control buttons as application windows. A document window always contains a title area and part of the scroll bar and ruler. Open window The document can be in an active or passive state. If the window is in a passive state (the title area is not highlighted in color), then by clicking on any part of it with the mouse, it will become in active state). Window
Menu The menu is one of the main elements of the graphical interface and is a list of commands. Selecting an item executes a certain team. If a menu command is followed by an ellipsis, selecting it will cause a dialog box to appear that allows the user to obtain or enter additional information.
Dialog panel Tabs Command buttons Lists Checkboxes Counter Sliders Switches Text fields Elements:
Tabs Dialog panels can include multiple "pages" called tabs. Dialogue panel
Command buttons Pressing a button (click) performs one or another action; the inscription on the button explains its meaning. Dialogue panel
Lists A list is a set of values offered for selection. The drop-down list looks like a text field with a button with a downward arrow. Dialogue panel
Checkboxes A checkbox allows you to assign a specific value to a parameter. They can be located either in groups or individually. The checkbox is shaped like a square; When a checkbox is checked, there is a “tick” in it. Dialogue panel
Counter The spinner is a pair of arrows that allow you to increase or decrease the value in the associated field. Dialogue panel
Sliders Allow you to smoothly change the value of any parameter. Dialogue panel
Switches Switches are used to select one of mutually exclusive options; the options are presented in the form of small white circles. The selected option is indicated by a circle with a dot inside. Dialogue panel
Text fields A text field is sometimes called an edit field and allows you to enter some text information. Dialogue panel
Context menu Object-oriented approach used in the operating room Windows system, allows you to treat drives, folders and files as objects. All these objects have certain properties, and certain operations can be performed on them.
End. Thank you for your attention.
WINDOWS Advantages. WINDOWS is a high-performance, multi-tasking, multi-threaded 32-bit object-oriented OS with a graphical interface and advanced networking opportunities. high-performance - works faster than others multitasking - can work with several programs simultaneously (write them into RAM) multi-threaded - allows, if there is a delay in the execution of one thread of commands solving a particular problem within a general task, to work with the next thread 32-bit system - the kernel contains 32-bit bit code, only some modules have 16-bit code for compatibility with MS-DOS mode object-oriented - the user works with documents, and the program (application) is considered as a tool for working with the document with a graphical interface - set graphic tools for interaction between user and computer
WINDOWS Interface elements ä Desktop with objects ä Main menu ä Office panel ä Taskbar with Start button - this is a set of tools with which the user communicates with the computer. An interface is a set of tools through which a user communicates with a computer.

WINDOWS All objects in Windows are presented in windows Main window elements ä ä Frame ä ä Title line ä ä System menu icon ä ä Title ä ä Collapse button ä ä Restore/Expand button ä ä Close button ä ä Menu bar ä ä Tool menu ä ä Horizontal and vertical scroll bars ä ä Status bar

WINDOWS Windows are of the following types: in the form of - a picture (icon) in the form of an icon - a picture (icon) in normal view - occupy part of the screen in normal view - occupy part of the screen in full-screen view - occupy the entire screen in full-screen view - occupy the entire screen

WINDOWS Windows in Windows are of the following types: - contain icons of folders, files and other programs Group - contain icons of folders, files and other programs - these are windows of applications and documents (you can work in them with your own hands) Application windows - these are windows of applications and documents (you can use them work put your hands on - these are windows in which the user communicates with the system (answers its requests or the system warns about non-standard situations) Dialog windows - these are windows in which the user communicates with the system (answers its requests or the system warns about non-standard situations)


WINDOWS Desktop Objects Regular folders Special folders Documents Shortcuts are similar to directories; they contain the names of other folders and files; they differ from regular ones in that they cannot be deleted and the names of some of them are reserved objects created in specific application a file containing information about the location and object for which it is created, provides Fast passage to the object

WINDOWS Special folders ä - contains icons of all objects located in the machine ä My Computer - contains icons of all objects located in the machine ä - contains icons of computers connected to this machine via the network ä Network Neighborhood - contains icons of computers connected to this machine via the network ä - designed to delete documents until it is emptied, the document can be restored to its old location ä Recycle Bin - designed to delete documents until it is emptied, the document can be restored to its old location

WINDOWS Actions with objects Objects can be: created open moved copy rename delete Three standard methods performing any actions: using operating menu- procedural method (p.File and p.Edit) using Drag&Drop technology using the context menu (right mouse button) select Before performing an action, the object must be selected

WINDOWS Creating a folder New folder can be created on the desktop or in any folder in several ways: ¶ ¶ Place the cursor on empty place in the desired folder and click right button Mouse, in the context menu that appears, select the New\Folder command. In the window that appears, under the new folder icon, enter its name and click ENTER key. · · Place the cursor in the desired folder, select the New\Folder command from the File menu. In the window that appears, under the new folder icon, enter its name and press ENTER.

WINDOWS Creating a shortcut A shortcut to a program, document or device can be created in any folder in several ways: ¶ ¶ Place the cursor on an empty space in the desired folder and press the right Mouse button, in the context menu that appears, select the Create\Shortcut command. In the Create shortcut window that appears, in the field Command line specify the name of the object for which the shortcut is being created, or click the Browse button to search for it. By pressing the Next button, select the name and icon for the shortcut, respectively, and then click the Finish button. · · Drag the object icon to the desired folder while holding down the CTRL+SHIFT keys. ¸ ¸ Drag the object icon to the desired folder and use the context menu command Create shortcut. ¹ ¹ Select the object, select the Copy command from the Edit menu. Go to the window where you intend to place the shortcut, select Insert Shortcut from the Edit menu.

WINDOWS Creating documents Create new document in any folder in several ways: ¶ ¶ Launch the program that will be used to develop the document, select the New command in the File menu Open the File menu item of any folder, select New\Document... Open context menu on the desktop, select New\Document...

