How to install full-fledged Linux on a flash drive. Full installation of Linux on a Flash drive
Very often people have the desire or need to install Ubuntu on a USB drive and be able to use their OS on any computer (as long as it is possible to boot from USB).
This article describes the process of installing Ubuntu on USB drives.
Some important notes And helpful information collected in the article Installing and using Ubuntu on a USB flash drive. It is worth familiarizing yourself with it before you start installing Ubuntu on a USB drive.
Preparing for installation
Download the system image from here. If you do not plan to run the system on machines with more than 4 GB random access memory It is preferable to choose 32-bit.
Burning an image
After the image has downloaded, it must be burned to a CD or USB drive.
On USB storage The easiest way to burn the image is with UNetbootin. This program is available for most popular operating systems (Windows, Linux, Mac) and is quite easy to use. All you need to do is specify the path to the downloaded image and select the disk on which the image will be written.
You can do without burning the image to any media by using a virtual machine, such as VirtualBox or QEMU. You just need to forward it to virtual machine USB drive. Further instructions will not change for this method.
Before booting, make sure that the BIOS selects USB or CD-ROM as the first boot device, depending on what you are booting from. You can get into the BIOS by pressing the Del key to desktop computers and F2 or F12 for laptops. For information on how to select a device to download, look on the Internet or read the instructions for your computer.
If everything is done correctly, you will see in front of you loaded with Live CD system.
Preparing a USB Drive
Launch the GParted program. 
Select the device you are going to install Ubuntu on. 
Format it to Ext2 or Ext4 file system. You can also divide the USB drive into 2 partitions so that it can be used for its intended purpose (transferring files from one computer to another). To do this, format the first partition in FAT32 (so that the partition is visible in Windows), and select the Ext2 or Ext4 file system for Ubuntu as the second partition. It is advisable to allocate at least 6 GB to the second partition so that you don’t have to worry about running out of space to install additional programs. 
It is hardly worth explaining the advantages of an operating system located on a compact removable media. It is perfect for a variety of purposes, and for advanced technical specialists may be irreplaceable. Running Ubuntu from a flash drive without installation is more than possible - all Linux users know this very well. But such a system has a minimal software package. Although working with command line is supported, the functionality of the solution may not be sufficient. But this is not difficult to fix.
Please note that USB drives are not designed for this role. The number of rewrite cycles for them is small, and they are not very resistant to breakdowns. This is the price to pay for cheapness and mobility. Therefore install on external storage The OS is not worth it for constant and serious work. The reason is simple - any operating system constantly stores temporary data on the media. The file system and changes are also logged. If you use a flash drive in a typical role, it will last for a long time.
IMPORTANT. It is better not to store important files on a flash drive with the OS. Having launched the OS, you can work with them in the cloud, or keep them on a separate drive.
You may ask - but how? solid state drives? The fact is that they are much more reliable. SSD drives designed for billions of rewrite cycles. Although they work using the same technology, they include useful features“self-protection” from wear.
The variety of Linux capabilities is a reason for the “envy” of other operating systems. We may not use special tools to perform launching Ubuntu from a flash drive, but use standard means.
IMPORTANT. At the beginning of the OS installation on external media make sure the system is not currently running from it.
After this, you can proceed with the installation as you would normally do it - from a “desktop” operating system. Settings will only be needed at the disk partitioning stage. Automatic marking must be disabled and selected instead manual method. If the media is correctly identified, then in the disk selection window it should be visible as /dev/sdb (/dev/sda is your primary disk with installed system). 

System improvement
Installing Ubuntu on a flash drive as a full-fledged OS turned out to be quite simple, right? But that is not all. You need to make sure that the speed will be acceptable and increase the service life of the drive. Now we will “conjure” the system already installed on the flash drive.
To begin, open the following configuration file:
Enter in the command line:
/dev/sdb1 / btrfs errors=remount-ro,noatime,nodiratime,compress=lzo,ssd,commit=60 0 1
This is the optimal set of instructions for working with SSD drives. We “look up to” them, because installing the OS on a USB flash drive is not initially provided.
You can also add settings for accessing RAM. They will help the system access the disk less often, using RAM more often for the same purposes:
$ sudo sysctl -w vm.laptop_mode=120
$ sudo sysctl -w vm.dirty_writeback_centisecs=12000
$ sudo sysctl -w vm.dirty_expire_centisecs=12000
ATTENTION. Don't forget to do it more often backup personal data on a flash drive! It will not be able to warn you before the final wear and death of memory blocks.
Possible problems
If it is important for you to install Ubuntu on a flash drive as a full-fledged OS, let us remind you once again - yes, you will receive the same OS as on desktop computer. She will be stable and safe. may not suit you.
Also, beware of these problems:
- Do not use file systems with a magazine for portable drives. This will have a very bad effect on their survivability. Journaling greatly increases the number of accesses to the file system.
- It is advisable to abandon the swap partition. It also generates a huge number of memory accesses. The installer will ask you to create it again. Give a negative answer.
IMPORTANT. If you accept the default settings, the PC will not be able to boot without an external drive.
conclusions
As you can see, if Ubuntu is installed correctly on a flash drive, it is not difficult to use it as a full-fledged OS; all that matters is the desire and the availability of a free USB drive. Some precautions are important only at first - in the future you can use the portable distribution just like any other. Just don't forget to back up your data.
Do you want to learn more Linux tricks? Then read the materials on our website, communicate with users in the comments and come visit more often!
Do you want to add more functionality to your flash drive? Have you always wanted something more than just putting files in for printing or copying? Did you know that you can install operating Linux system to your USB drive and bring it wherever you want? Plus, did you know that you can install "portable" versions of your favorite apps on a USB drive? So whenever you borrow someone's computer and don't have your favorite browser, you can just plug in the flash drive and all your settings will automatically be set the way you want them! With these instructions you can do it easily!
- USB flash drive with a minimum capacity of 4 GB. 8 GB or more recommended. The bigger, the better.
- Internet connection.
- Computer under managed by Microsoft Windows.
You've probably heard of Linux. It is a kind of operating system similar to Windows. Linux comes in a variety of forms called distributions. The most common of which is Ubuntu. Ubuntu is what we will install on your flash drive.

On a note! It would be better if you save it in the same location as the Ubuntu ISO, and even better if they are both on your desktop.
Step 3. Install the OS on a USB device
Now that you have prepared everything for, it's time to connect the flash drive. Before starting, do backup copy your content to your computer to save your important data.
Now double-click on the USB installer you downloaded in the previous step, click Yes if Account Control prompts you to allow the program to make changes on your PC.

Now let's do it step by step:
- On the first screen, click "I Agree".

- After that it will allow you to choose Linux distribution from the drop down list, click on it and select "Ubuntu".

- Ignore the "Download the iso" option, since you've already done that. Now click the Browse button and navigate to the location where you saved ISO file Ubuntu, then double click it.


- Now be careful in this step because you may get confused if you have any other flash drives. Next, click on the drop-down list where you will select the drive letter of your flash drive.


On a note! Pay attention to the “Format X: Drive” parameter (where X is the letter of your flash drive).
- Determine the space on the flash drive for the operating system by moving the slider in the “Step 4” section to the desired amount.

- After that, click “Create” to start the installation.

- A dialog box will appear telling you what the installer will do with your flash drive, this is normal. After reading, click "Si".

- Relax and let the installer do his job. Once recording is complete, click Close.

When you check your flash drive, it will probably have less space than before, obviously because you installed the OS there.
Step 4. Testing Ubuntu
Now that Linus is installed on your flash drive, why not test it? Be aware that this part gets tricky. So:
- Remove the flash drive and turn off the computer.
- When it turns off, plug the flash drive back in, then turn on the computer.
- Once you press the power button, keep pressing F10 (or F12, it depends on your computer) to access the BIOS. The BIOS (or Basic Input Output System) can look quite strange due to all the text on blue screen(depends on motherboard) And complete absence graphics, as well as the fact that you have to use the keyboard to navigate the menus.

- Once you have entered the BIOS, go to the System Configuration menu.

- Look for "Boot Options" or something similar. This will take you to another menu.

- Then go to "Boot Order" or "Boot Priority" (depending on your computer's motherboard).

- Once you've found it, change your system boot order to " USB Flash Drive" or " USB Disk Key" or something similar was at the very top of the list, meaning it should be first in terms of loading priority.



- After this, save the changes and restart your computer.

- You will then be greeted with the Ubuntu installer boot menu, where you must select the first option “Run Ubuntu without installing”.

After a few loading screens (matrix style messages will appear), you will see the desktop. Congratulations!
- So, go to the following link http://portableapps.com/suite, scroll down the list a bit and click on which version of the suite you want (Standard Suite is recommended).


Click “Download Now - Free”
- Once the download is complete, double-click the installer.

- On the first screen, click Next.


- On the second, select “I Accept.”

- In the window that opens, by default the item “ New installation", leave it, click "Next".

- Leave the checkbox next to “Portable - install to USB drive”, click “Next”.

Leave the checkbox on “Portable - install to USB drive”
- In the window that appears, the installer automatically detected the flash drive, leave a checkmark on the name of the flash drive, click “Next”.

- Click Install.

- Once everything is installed, click “Finish” and the portable set of applications will launch. It's very similar to the Windows Start menu, so it shouldn't be too difficult to figure out.

Step 6: Install/Add New Portable Applications
Portable versions of the applications are available at http://portableapps.com.

- Use the search bar on the right top corner to find the application you need.

- Once you have found it, click the "Download" button.

- The application will be saved in the “.paf.exe” format. Double click it to install.

- Follow the installer's instructions.

- Click the "Browse" button, select your flash drive, click "Install".



Made! Now on your flash drive is a portable operating system with all the programs you need.
Video - Installing Ubuntu on a USB flash drive
Ubuntu is a fairly lightweight operating system whose installation is simple and quick. Each a new version LINUX is designed with the most simplified installation option.
The given instructions describe this process in detail, starting from creating an image on a flash drive, to full load operating system.
The most difficulties can arise during disk partitioning or installation of Ubuntu Linux next to Windows. These and other problems that may arise during the download process are discussed at the end of the article.
Brief Definition
Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux operating system. Its primary task is to provide a convenient, powerful, but at the same time simple interface for working with a computer.
The advantages include:
- accessibility, since it is completely free and does not require any activation;
- auto-update applications as needed;
- easy installation of programs;
- high protection against viruses.
Preparing for installation
Installing Linux Ubuntu from a flash drive has more advantages compared to the previously popular installation from a CD:
- modern laptops and netbooks often do not have disk drives;
- installation from a USB device is much faster than from a disk;
- A CD quickly fails due to scratches and other defects.
To begin the installation, you need to create a bootable USB flash drive. To do this, you will need a Linux disk image or a CD with it that you can copy.
The general Linux installation process is as follows:
- downloading/copying a system image;
- Creation bootable flash drive;
- changing BIOS settings;
- Linux installation.
It is best to download the system image from its official website, since the newest and most improved version is provided there. You should also take into account the parameters of your computer, as new versions of software may not work well with outdated equipment.
Video: Creating a bootable USB flash drive with OS
Burn image
The flash drive for recording must be at least 1 GB in size. The downloaded image can be recorded using the following programs:
- Pendrive;
- Unetbootin;
- Lili USB Creator;
- UltraIso;
- Universal USB Installer.
Creating an image in Windows
The Unetbootin program is suitable for creating a boot device like in an operating room Windows system, and in Ubuntu. It must be downloaded, installed and launched. After that, in the “Diskimage” item, select required file systems. Among the disks in “Drive”, select the desired boot device and confirm the creation of the image:

This program has the advantage that it does not require formatting the device, but creates next to already existing files their. After finishing recording, you can begin the installation itself.
Creating a bootable USB flash drive
If the flash drive is created from a computer where there is any Linux version, you can also use the previous method, or you can do it differently. Eat special utility usb-creator-gtk. To launch it, you need to hold down ALT+F2 and enter “usb-creator-gtk” or in the application menu find “Create a boot disk”:

In the program itself, specify the location where the Linux ISO image file is located and select the USB device in the window just below:

After that, click “Create boot disk" and the program will start working.
Bootloader in BIOS
The next step is to switch to BIOS device, from which the download begins. On some computers this is done automatically, just insert the USB flash drive, reboot the device and go to boot menu, which opens when you press Esc, Tab or F8:
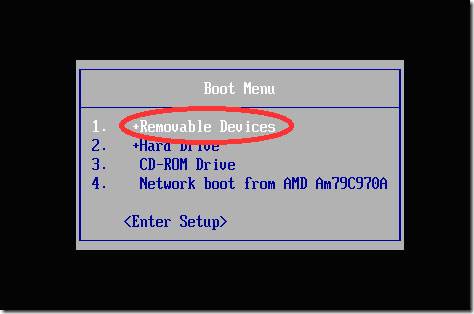
But it happens that there is no such option on the computer, so when booting you need to go into the BIOS. For different devices The BIOS structure and input combinations may differ, but usually these are the Del / F2 / F12 keys:

In the window that opens, press the “right” key and go to the “Boot” item:
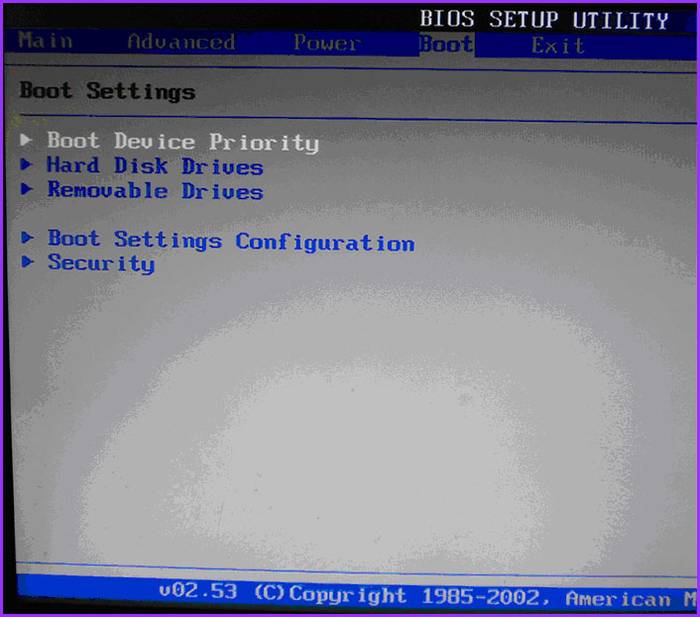
- in it select the item “ Hard Disk Drives";
- in the menu that appears, press Enter on “1st Drive”;
- a list will open in which you need to select the name of the bootable USB device;
- press Enter and Esc:

The computer will automatically reboot and start from the USB device.
How to install LINUX Ubuntu from a USB flash drive
As soon as the flash drive boots, the following window will open with a choice of language and the next action:

To install the operating system, click on desired language and "Install Ubuntu". Next, a window will open with the title “Preparing for installing Ubuntu", in which you need to make sure that the computer has enough free space on the hard drive and it is connected to the Internet.
If the computer is not connected to the network via Wi-Fi, then at this stage there will be no Internet, but this is not so scary, since it is needed for downloading latest updates, which can be done later.
Bottom item “Install this third party” software“It’s better to check the box, then additional software will be installed.
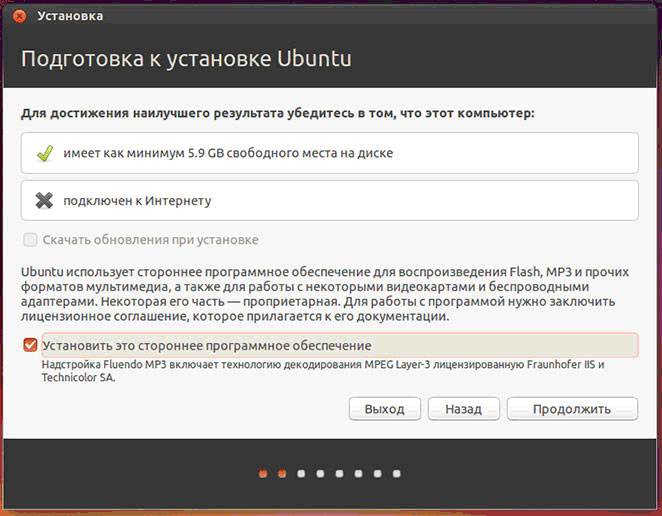
The next step is the installation option:

Installation next to Windows
If you want to have two operating systems and select the one you need when starting, then click the first item. Next you need to adjust the size of the partitions of your hard drive. Advanced users can partition the disk themselves using the advanced partition editor, but this is not recommended for others.
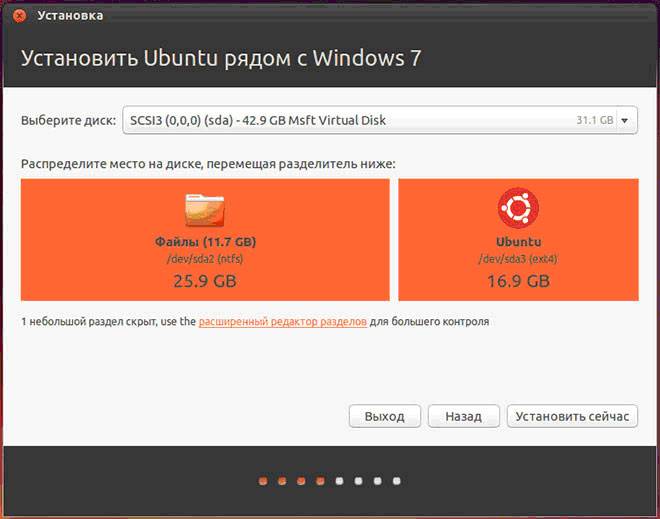
After clicking “Install Now”, a warning will pop up about creating and changing partitions on the disk; this may take a long time. Continue installing the system, after a while you will need to select regional standards for Ubuntu Linux - time zone and keyboard layout. Then you will need to create a user and password to log into Linux. Fill out all forms and click “Continue”:
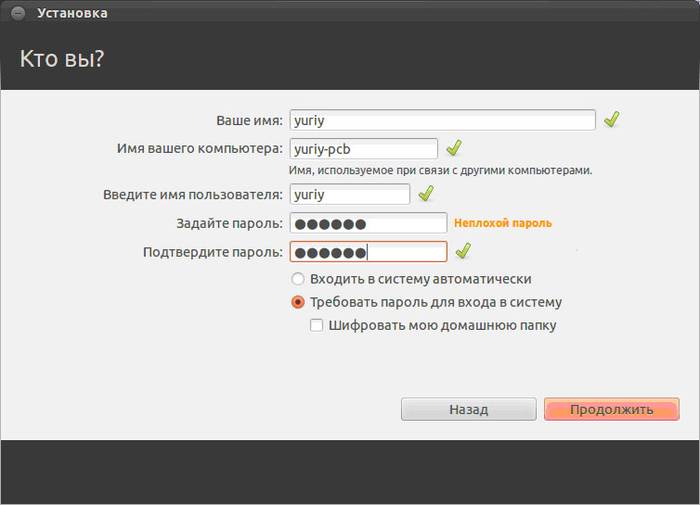
Next you should select an image for your user:

The installer will also prompt you to import Accounts from other operating systems:

After the process is completed, you will need to restart your computer, remembering to remove the bootable USB flash drive.

Replacing the current OS with Linux
Pre-prepare clean HDD or disk with unnecessary information. Then, when choosing the installation type, click “Erase disk and install Ubuntu”, and then the steps will proceed as in the instructions above.
Another installation option
When you select the last item, a window opens:
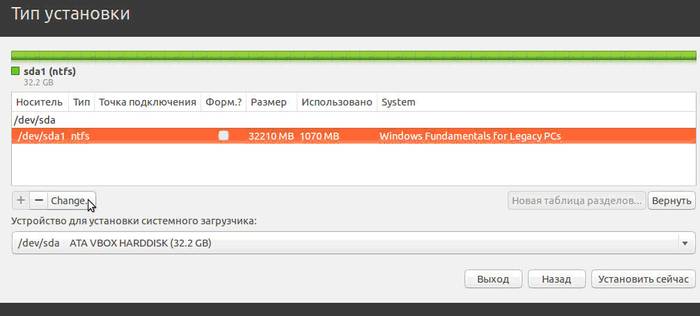
This is the structure of the available hard drives and their sections. The screenshot shows a computer with one hard drive/dev/sda, which has one partition /dev/sda1 and Windows is installed on it. In other words – Disk C. The number of partitions and disks may vary. Ntfs – disk extension type. The task is to select from the available partitions the appropriate one in order to allocate 10 GB for new system. Click the section and the “Change” button:
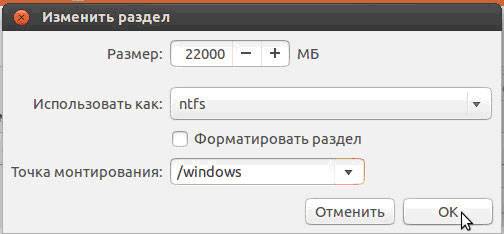
- in the “Size” section indicate right size disk;
- in the “Use as” column, select desired type disk, in this case “ntfs”;
- Don’t check the “Format” box if you don’t want to lose all your data;
- at the mount point, select “/windows” to have access to your files from the program;
- Click "OK".
Confirm your actions:
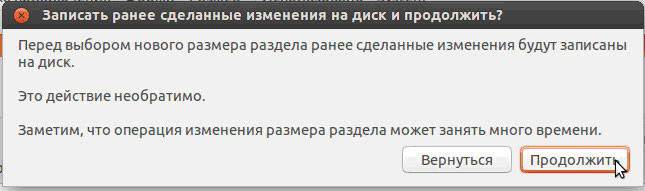
Now there is free space in the disk table:
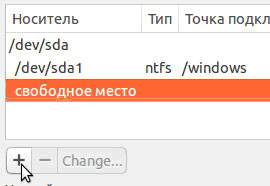
Choose new item and click “+”, another window will open:

It is designed to create a swap partition, which is used in case of insufficient RAM. Place it as shown in the picture. Click "OK".
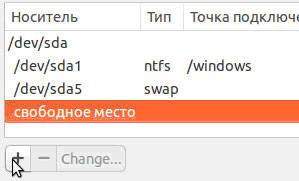

The final view of the list of sections is this:
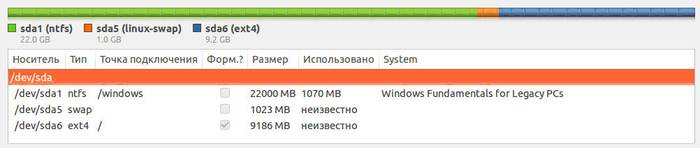
Place the Format checkbox only where you need to erase data.
Launching Linux
If Linux is the only operating system, it will boot immediately. If not, there will be four download options:
- Ubuntu system
- recovery mode, similar safe mode on Windows
- running a RAM test
You can wait 10 seconds and Linux will load automatically, or you can select the desired item yourself.
When starting, the computer will ask for a password to log in:

After this, the desktop will load.
Possible installation problems
If the program does not start when installing from a flash drive, the reason may be:
- bad flash drive;
- incorrectly recorded image;
- incorrectly loaded system image.
You can only find the reason experimentally. If you have another flash drive, write the image to it and try installing it. If the system continues to not start from the flash drive, check to see if the required image was downloaded for your computer at all. Still not working? There are cases that the problem is in the image recording process itself. From the programs listed at the beginning of the article, try to record and run the image from a USB device one by one. In any case, the problem is one thing.
If when trying launch Linux After installing the system, a black screen appears and nothing else happens, the problem may be in the driver of the installed video card.
To resolve this issue, hold down the left Shift key to display the GRUB menu before loading the OS. Move the cursor to the top point and press the "e" key. This is needed to edit boot parameters.
After “quiet splash” you need to add “nomodeset”:
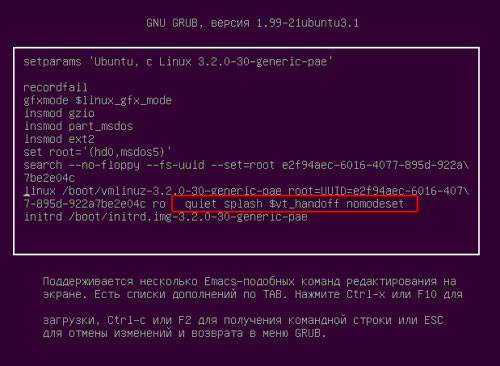
After that, press “F10” to load the OS with the entered parameters, this makes it possible to install proprietary video card drivers in the “System Settings” -> “Device Drivers” menu. Now you need to reboot the system. operating system Ubuntu LINUX– simple and straightforward to use, installing it from a flash drive is quite quick and easy. Minor problems may occur during and after installation, but they are easy to fix.
>Ubuntu is a fairly lightweight operating system whose installation is simple and quick. Each new version of LINUX is developed with the most simplified installation option.
The instructions provided describe this process in detail, from creating an image on a flash drive to fully loading the operating system.
The most difficulties can arise during disk partitioning or installation of Ubuntu Linux next to Windows. These and other problems that may arise during the download process are discussed at the end of the article.
Brief Definition
Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux operating system. Its primary task is to provide a convenient, powerful, but at the same time simple interface for working with a computer.
The advantages include:
- accessibility, since it is completely free and does not require any activation;
- auto-update applications as needed;
- easy installation of programs;
- high protection against viruses.
Preparing for installation
Installing Linux Ubuntu from a flash drive has more advantages compared to the previously popular installation from a CD:
- modern laptops and netbooks often do not have disk drives;
- installation from a USB device is much faster than from a disk;
- A CD quickly fails due to scratches and other defects.
To begin the installation, you need to create a bootable USB flash drive. To do this, you will need a Linux disk image or a CD with it that you can copy.
The general Linux installation process is as follows:
- downloading/copying a system image;
- creating a bootable flash drive;
- changing BIOS settings;
- Linux installation.
It is best to download the system image from its official website, since the newest and most improved version is provided there. You should also take into account the parameters of your computer, as new versions of software may not work well with outdated equipment.
Video: Creating a bootable USB flash drive with OS
Burn image
The flash drive for recording must be at least 1 GB in size. The downloaded image can be recorded using the following programs:
- Pendrive;
- Unetbootin;
- Lili USB Creator;
- UltraIso;
- Universal USB Installer.
Creating an image in Windows
The Unetbootin program is suitable for creating a boot device in both the Windows and Ubuntu operating systems. It must be downloaded, installed and launched. After that, in the “Diskimage” item, select the desired system file. Among the disks in “Drive”, select the desired boot device and confirm the creation of the image:

This program has the advantage that it does not require formatting the device, but creates its own files next to existing ones. After finishing recording, you can begin the installation itself.
Creating a bootable USB flash drive
If the flash drive is created from a computer running any version of Linux, you can also use the previous method, or you can do it differently. There is a special utility usb-creator-gtk. To launch it, you need to hold down ALT+F2 and enter “usb-creator-gtk” or in the application menu find “Create a boot disk”:

In the program itself, specify the location where the Linux ISO image file is located and select the USB device in the window just below:

After that, click “Create a boot disk” and the program will start working.
Bootloader in BIOS
The next step is to switch the device from which the boot starts in the BIOS. On some computers this is done automatically, just insert the USB flash drive, reboot the device and during boot go to the boot menu, which opens when you press Esc, Tab or F8:

But it happens that there is no such option on the computer, so when booting you need to go into the BIOS. For different devices, the BIOS structure and input combinations may differ, but usually these are the Del / F2 / F12 keys:

In the window that opens, press the “right” key and go to the “Boot” item:

- in it select the item “Hard Disk Drives”;
- in the menu that appears, press Enter on “1st Drive”;
- a list will open in which you need to select the name of the bootable USB device;
- press Enter and Esc:

The computer will automatically reboot and start from the USB device.
How to install LINUX Ubuntu from a USB flash drive
As soon as the flash drive boots, the following window will open with a choice of language and the next action:

To install the operating system, click on the desired language and “Install Ubuntu”. Next, a window called “Preparing to install Ubuntu” will open, in which you need to make sure that your computer has enough free space on your hard drive and is connected to the Internet.
If the computer is not connected to the network via Wi-Fi, then at this stage there will be no Internet, but this is not so scary, since it is needed to download the latest updates, which can be done later.
It is better to check the bottom item “Install this third-party software”, then additional software will be installed.

The next step is the installation option:

Installation next to Windows
If you want to have two operating systems and select the one you need when starting, then click the first item. Next, you need to adjust the partition size of your hard drive. Advanced users can partition the disk themselves using the advanced partition editor, but this is not recommended for others.

After clicking “Install Now”, a warning will pop up about creating and changing partitions on the disk; this may take a long time. Continue installing the system, after a while you will need to select regional standards for Ubuntu Linux - time zone and keyboard layout. Then you will need to create a user and password to log into Linux. Fill out all forms and click “Continue”:

Next you should select an image for your user:

The installer will also offer to import accounts from other operating systems:

After the process is completed, you will need to restart your computer, remembering to remove the bootable USB flash drive.

Replacing the current OS with Linux
Prepare a blank hard drive or a drive with unnecessary information in advance. Then, when choosing the installation type, click “Erase disk and install Ubuntu”, and then the steps will proceed as in the instructions above.
Another installation option
When you select the last item, a window opens:

This is the structure of the existing hard drives and their partitions. The screenshot shows a computer with one hard drive /dev/sda, one partition /dev/sda1 and Windows installed on it. In other words – Disk C. The number of partitions and disks may vary. Ntfs – disk extension type. The task is to select from the available partitions the appropriate one in order to allocate 10 GB to the new system. Click the section and the “Change” button:

- in the “Size” item, indicate the desired disk size;
- in the “Use as” column, select the desired disk type, in this case “ntfs”;
- Don’t check the “Format” box if you don’t want to lose all your data;
- at the mount point, select “/windows” to have access to your files from the program;
- Click "OK".
Confirm your actions:

Now there is free space in the disk table:

Select a new item and click “+”, another window will open:

It is designed to create a swap partition, which is used in case of insufficient RAM. Place it as shown in the picture. Click "OK".


The final view of the list of sections is this:

Place the Format checkbox only where you need to erase data.
Launching Linux
If Linux is the only operating system, it will boot immediately. If not, there will be four download options:
- Ubuntu system
- recovery mode, similar to safe mode in Windows
- running a RAM test
You can wait 10 seconds and Linux will load automatically, or you can select the desired item yourself.
When starting, the computer will ask for a password to log in:

After this, the desktop will load.
Possible installation problems
If the program does not start when installing from a flash drive, the reason may be:
- bad flash drive;
- incorrectly recorded image;
- incorrectly loaded system image.
If, when you try to start Linux after installing the system, a black screen appears and nothing else happens, the problem may be with the driver of the installed video card.
To resolve this issue, hold down the left Shift key to display the GRUB menu before loading the OS. Move the cursor to the top point and press the "e" key. This is needed to edit boot parameters.
After “quiet splash” you need to add “nomodeset”:

After that, press “F10” to load the OS with the entered parameters, this makes it possible to install proprietary video card drivers in the “System Settings” → “Device Drivers” menu. Now you need to reboot the system. The Ubuntu LINUX operating system is simple and easy to use, and installing it from a flash drive is quite quick and easy. Minor problems may occur during and after installation, but they are easy to fix.
